Figure 6.
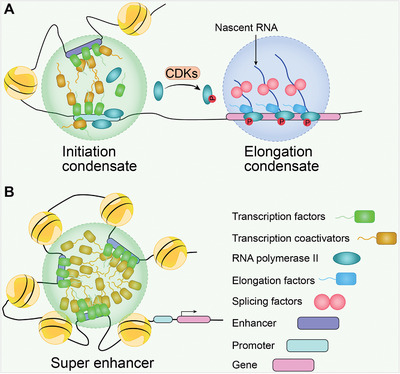
LLPS in gene transcription. A) Transcriptional condensates. Transcriptional condensates consist of initiation condensates and elongation condensates. Transcription factors (TFs) containing IDRs are prone to phase separation. TFs bind to regulatory elements such as enhancers and promoters to establish initiation condensates. Then, coactivators and unphosphorylated RNAPIIs are recruited. RNAPIIs are phosphorylated at the carboxy‐terminal domain by cyclin‐dependent kinases CDKs, which launches the transition from initiation condensates to elongation condensates. The elongation condensate is formed by phosphorylated RNAPIIs, elongation factors, nascent RNA, and splicing factors. B) Super enhancers (SEs). SEs are defined as clusters of enhancers enriched with TFs, coactivators, and RNAPIIs that drive robust genes expression in carcinogenesis.
