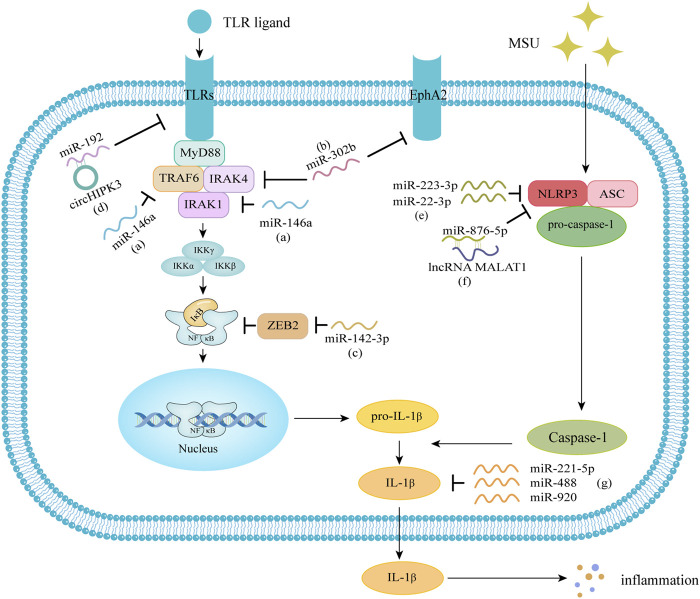
FIGURE 1.
Molecular mechanisms of miRNA in gout. (A) miR-146a downregulates the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and the NLRP3 inflammasome through the TLR/NF-κB signaling pathway. (B) miR-302b can negatively regulate the transcription and maturation of IL-1β by targeting IRAK4 and EphA2. (C) miR-142-3p can target and negatively regulate ZEB2, regulate NF-κB signaling, and lead to increased expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. (D) circular RNA circHIPK3 can act as a molecular sponge to bind miR-192, regulate the expression of TLR4. (E) miR-223-3p and miR-22-3p can directly inhibit the expression of NLRP3 to reduce the release of IL-1β. (F) lncRNA MALAT1 can reduce the inflammatory response through the miR-876-5p/NLRP3 pathway. (G) miR-221-5p, miR-488 and miR-920 can interact with the 3′ UTR of IL-1β and can target and inhibit IL-1β. MiRNA, microRNA; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing 3; TLR, Toll-like receptor; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; IRAK4, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4; EphA2: Ephrin type-A receptor 2; ZEB2, zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2; lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.