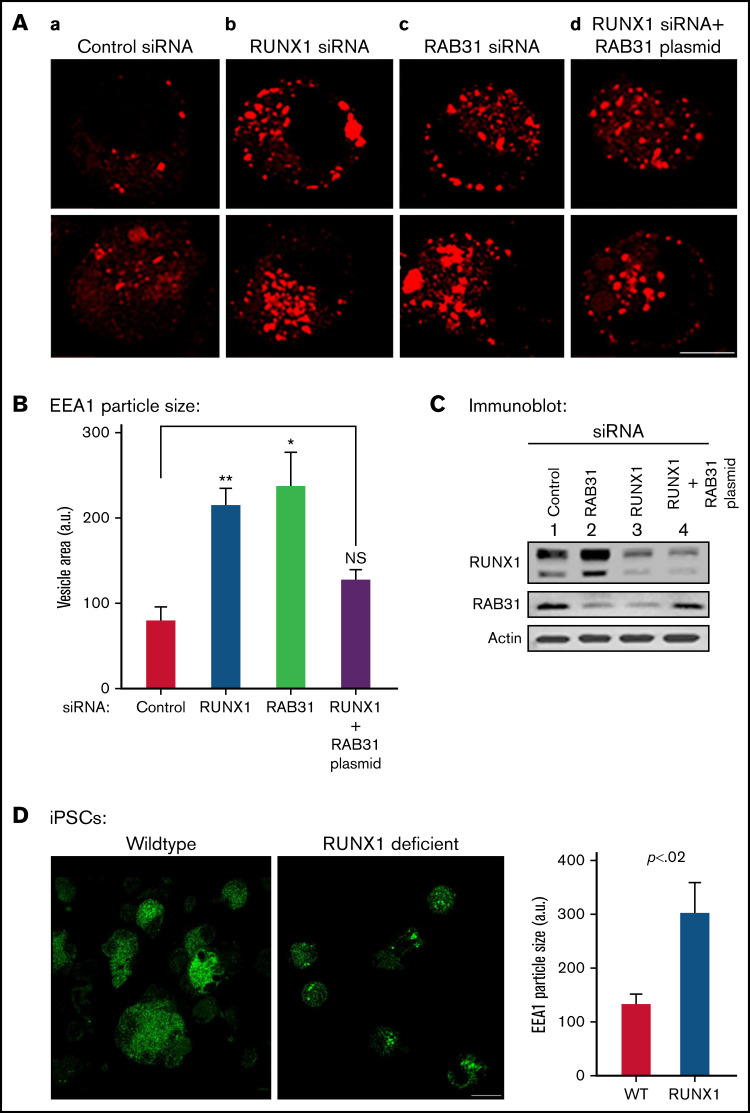
Figure 4.
Effect on EE morphology on siRNA knockdown of RUNX1 or RAB31 in megakaryocytic HEL cells and in iMK differentiated from WT and RHD iPSCs. (A) Immunofluorescence studies on the effects of siRNA knockdown of RUNX1 and RAB31 in megakaryocytic HEL cells immobilized on coverslips and stained for EEA1 in: (a) control cells; (b) cells treated with RUNX1 siRNA, showing striking enlargement of EEA1 particles; (c) cells treated with RAB31 siRNA, showing similar alteration in EEs; and (d) RUNX1-depleted cells with RAB31 reconstitution showing partial reversal of EEA1 abnormality. In each column, 2 random examples of cells are shown. (B) Quantification of the size of EEA1 particles with RUNX1 or RAB31 depletion by siRNAs and with RAB31 reconstitution by RAB31 plasmid in RUNX1-depleted cells is shown. Presented as mean ± standard error of the mean of 3 independent experiments. (C) Immunoblotting showing RUNX1, RAB31, and actin (loading control) in control cells and with knockdown of RUNX1 or RAB31 and after RAB31 reconstitution in RUNX1-depleted cells. (D) Early endosomal defect in iMKs differentiated from iPSCs generated from a patient with RUNX1 mutation (RHD) compared with those from WT iPSCs. Scale bar = 10 µm. P values (*P < .001; **P < .0001) are for comparisons with control siRNA. NS, not significant.