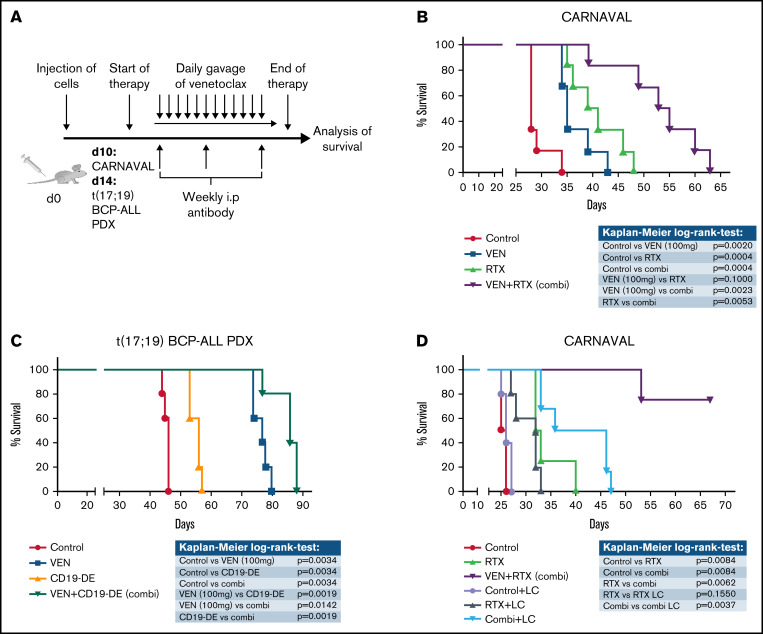
Figure 3.
Combination of VEN and antibodies in xenograft mice in vivo. (A) Experimental scheme: CARNAVAL cells or t(17;19) BCP-ALL PDX were injected IV into NSG mice. VEN (100 mg/kg per day) was given daily via oral gavage. Therapeutic antibodies (1 mg/kg) were applied weekly via the intraperitoneal route. (B) CARNAVAL cells were injected into NSG mice and left untreated (control), treated with 100 mg/kg per day VEN, 1 mg/kg per week RTX, or the combination (combi) of both. (C) One t(17;19)-positive BCP-ALL PDX sample was injected into NSG mice and either left untreated (control), treated with 100 mg/kg per day VEN, 1 mg/kg per week CD19-DE, or the combination (combi) of both. (D) NSG mice were injected with CARNAVAL cells. Animals were left untreated (control), treated with RTX (1 mg/kg per week intraperitoneal), VEN (100 mg/kg per day oral gavage), or the combination (VEN+RTX). For macrophage depletion, mice received weekly injection of LC (100 µL/wk intraperitoneally, i.p.). Survival was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank statistics. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. n, animals per group.