Figure 5.
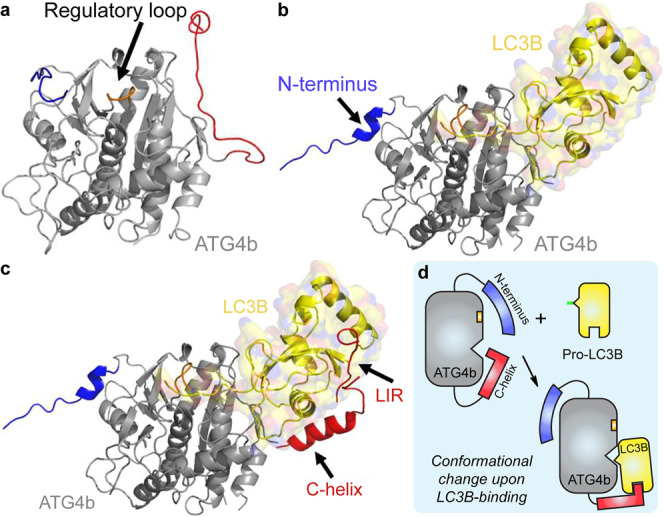
Structural model for the LC3B-ATG4b interaction. (a) X-ray structure of apo-ATG4b (2CY7). (b) X-ray crystal structure of pro-LC3B/ATG4b-354 (2ZZP). The main body of ATG4b is shown in gray and LC3B is shown in yellow. Upon LC3B binding, the N-terminal tail (blue) and the regulatory loop (orange) of ATG4b undergo conformational changes. The C-terminal tail (red) is deleted in the complex structure. (c) Model of full-length ATG4b-LC3B. The model is built from 2CY7, 2ZZP, the ATG7c/LC3 complex (3RUI), and the LC3/p62 peptide complex “LIR” (2ZJD). We hypothesize that the C-terminus (residues 355–393) of ATG4b binds to the back of LC3, perhaps forming a helix, as is seen in the complex of ATG7c bound to LC3. Images were made using Pymol. (d) Schematic illustration of the binding modes described in (a∼c).
