Fig. 1.
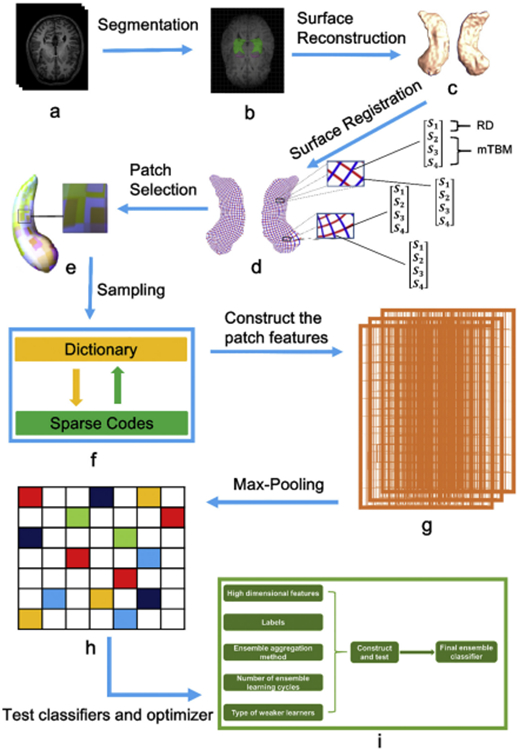
The whole pipeline applied in this paper. Subplots: (a) T1 MRIs; (b) segmentation of bilateral hippocampus; (c) reconstruction of 3D surface models; (d) one to one correspondence obtained from surface registration (the red curves are the isoparametric curves and therefore they are perpendicular to the medial axis; the intersection of each red curve and blue curve represents a surface vertex; each vertex contains a 4 × 1 vector that represents by S1, S2, S3 and S4); (e) selection of patches; (f) sparse coding and dictionary learning; (g) construction of patch features; (h) Max-pooling; (i) selection of suitable ensemble classifiers and optimizers.
