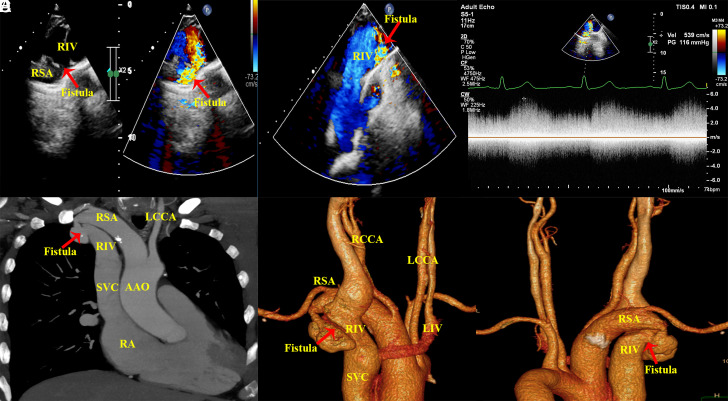
Figure 1.
(A and B) Transthoracic and color Doppler echocardiography show subclavian artery to innominate vein fistula. (C) Continuous-wave Doppler shows a flow signal at 5.4 m/s that is continuously moving from the RSA to the RIV throughout the cardiac cycle. Maximum intensity projection (D) and 3-dimensional reconstruction (E and F) show an arteriovenous fistula from the RSA to the RIV associated with proximal stenosis and distal aneurysmal dilatation of the fistula vessels. RSA, right subclavian artery; RIV; right innominate venous; LIV, left innominate venous LCCA, left common carotid artery; RCCA, right common carotid artery; AAO, ascending aorta; SVC, superior vena cava.

 Content of this journal is licensed under a
Content of this journal is licensed under a