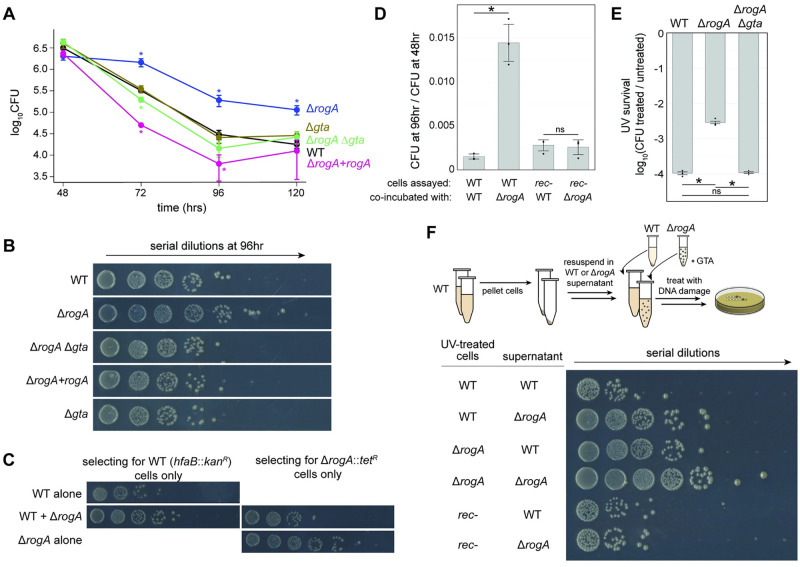
Fig 5. GTAs provide a long-term survival benefit.
(A) Survival of various strains in PYE over several days (n ≥ 3, error bars indicate SD). * = p-value <0.05 comparing data of same time point to wild type. Data are available in S1 Data. (B) Representative images of cell survival after 96 h in PYE. (C) Survival of wild-type (hfaB::kanR) or ΔrogA::tetR cells when grown together or alone. Cells were enumerated on plates containing either kanamycin or tetracycline to select for either wild-type or ΔrogA cells. (D) Survival of the wild type (hfaB::kanR) or the recombination-deficient rec526 strain in combination with either wild-type or ΔrogA cells in stationary phase (n = 3, error bars indicate SD). * = p-value <0.05 between indicated data. ns = not significant. Data are available in S1 Data. (E) Survival of different strains in response to high levels of UV during stationary phase. Survival rates are plotted as the (CFU after treatment)/(CFU before treatment) (n = 3, error bars indicate SD). * = p-value <0.05 between indicated data. ns = not significant. Data are available in S1 Data. (F) Schematic for treating cells with UV after providing supernatants from different cultures. Survival of different strains with supernatant from either wild-type or ΔrogA stationary phase cultures. CFU, colony-forming unit; GTA, gene transfer agent.