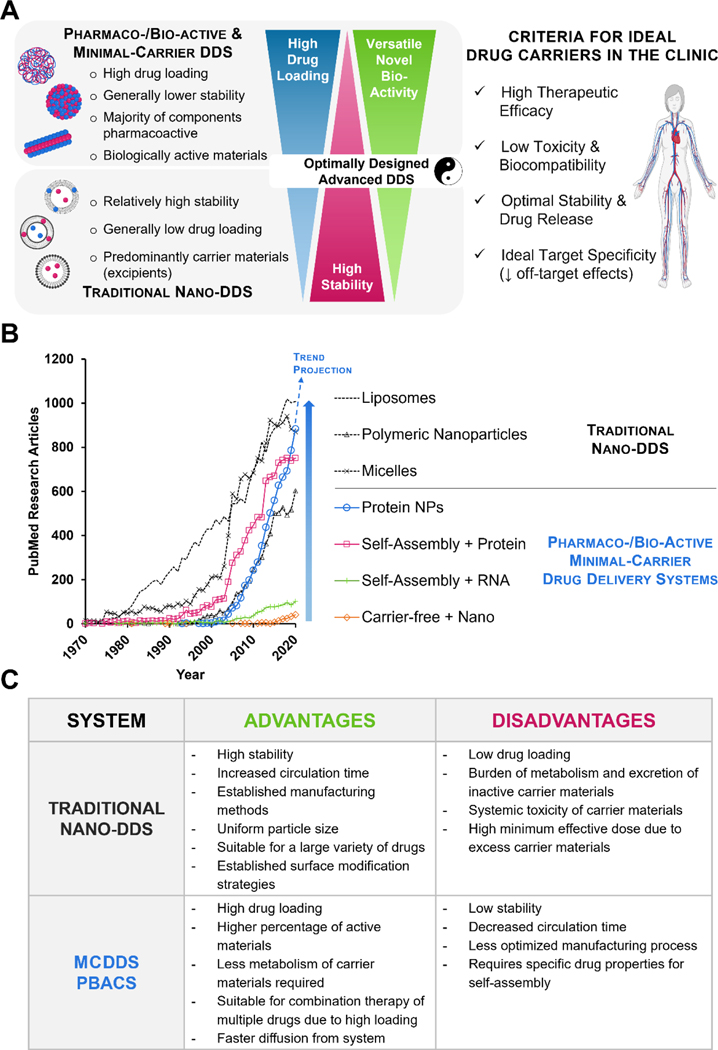
Figure 1. Emerging nanosized minimal-carrier and pharmacoactive drug delivery systems compared to traditional drug delivery systems.
(A) Comparisons between traditional nano-DDS and MCDDS/PBACS highlighting the contrasting and complementary features of both systems. Optimized combinatorial systems could lead to ideal drug carrier candidates for clinical translation. (B) The emerging trend of MCDDS and PBACS, especially protein therapeutics, is fast approaching the gold-standard polymeric drug delivery systems in recent years. *PubMed search terms: Liposome, (liposome[Title/Abstract]) NOT (review[Publication Type]); Polymeric nanoparticles, (Polymeric nanoparticle[Title/Abstract]) OR ((PLGA[Title/Abstract] AND (drug[title/abstract])) NOT (review[Publication Type]); Micelles, (Micelle[title/abstract]) NOT (review[Publication Type]); Protein NPs, (protein[Title/Abstract]) AND (nanoparticle[Title/Abstract]) NOT (review[Publication Type]) NOT (albumin[Title/Abstract]); Self-Assembly + Protein, (self-assembl*[Title/Abstract]) AND (protein[Title/Abstract]) NOT (review[Publication Type]); Self-Assembly + RNA, (self-assembl*[Title/Abstract]) AND (RNA[Title/Abstract]) NOT (review[Publication Type]); Carrier-free + Nano, (Carrier-free[Title/Abstract]) AND (nano*[Title/Abstract]) NOT (review[Publication Type]). (C) Comparison of traditional nano-DDS and MCDDS.