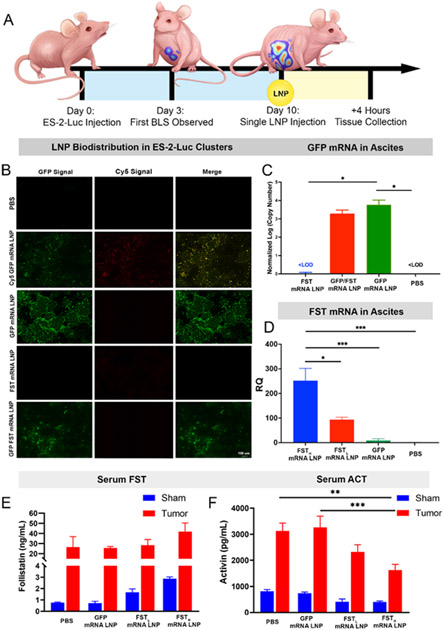
Figure 2. Efficient LNP-mediated delivery of FST mRNA leads to a superior therapeutic effect, demonstrated by serum ActA reduction.
(A) Experimental design illustrating ES-2-Luc bearing mice receiving a single mRNA LNP dose (GFP mRNA, Cy5-GFP mRNA, GFP/FST mRNA, and FST mRNA, 10 μg total mRNA equivalents per dose per mouse). Four hours after IP injection, sera and ascitic fluid were collected for analysis. (B) Fluorescence images of ES-2-Luc clusters 4 h after a single injection with the LNPs loaded with the indicated mRNAs. (C) Absolute qRT-PCR quantification of GFP mRNAs in ES-2-Luc clusters 4 h after IP injection of PBS and LNPs loaded with 0 μg GFP mRNA (FST mRNA LNP), 5 μg GFP mRNA (GFP/FST mRNA LNP), and 10 μg GFP mRNA (GFP mRNA LNP). (D) Relative qRT-PCR quantification of FST mRNAs in ES-2-Luc clusters 4 h after IP injection of PBS and LNPs loaded with 10 μg FST mRNA (FSTH mRNA LNP), 5 μg FST mRNA (FSTL mRNA LNP), or 0 μg FST mRNA (GFP mRNA LNP). Expressed as mean ± SEM, n=5, *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (E) FST and (F) ActA serum protein concentrations expressed as mean ± SEM, n=5, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test.