Figure 2. PC signature in LUADs predicts better survival and response to immunotherapy.
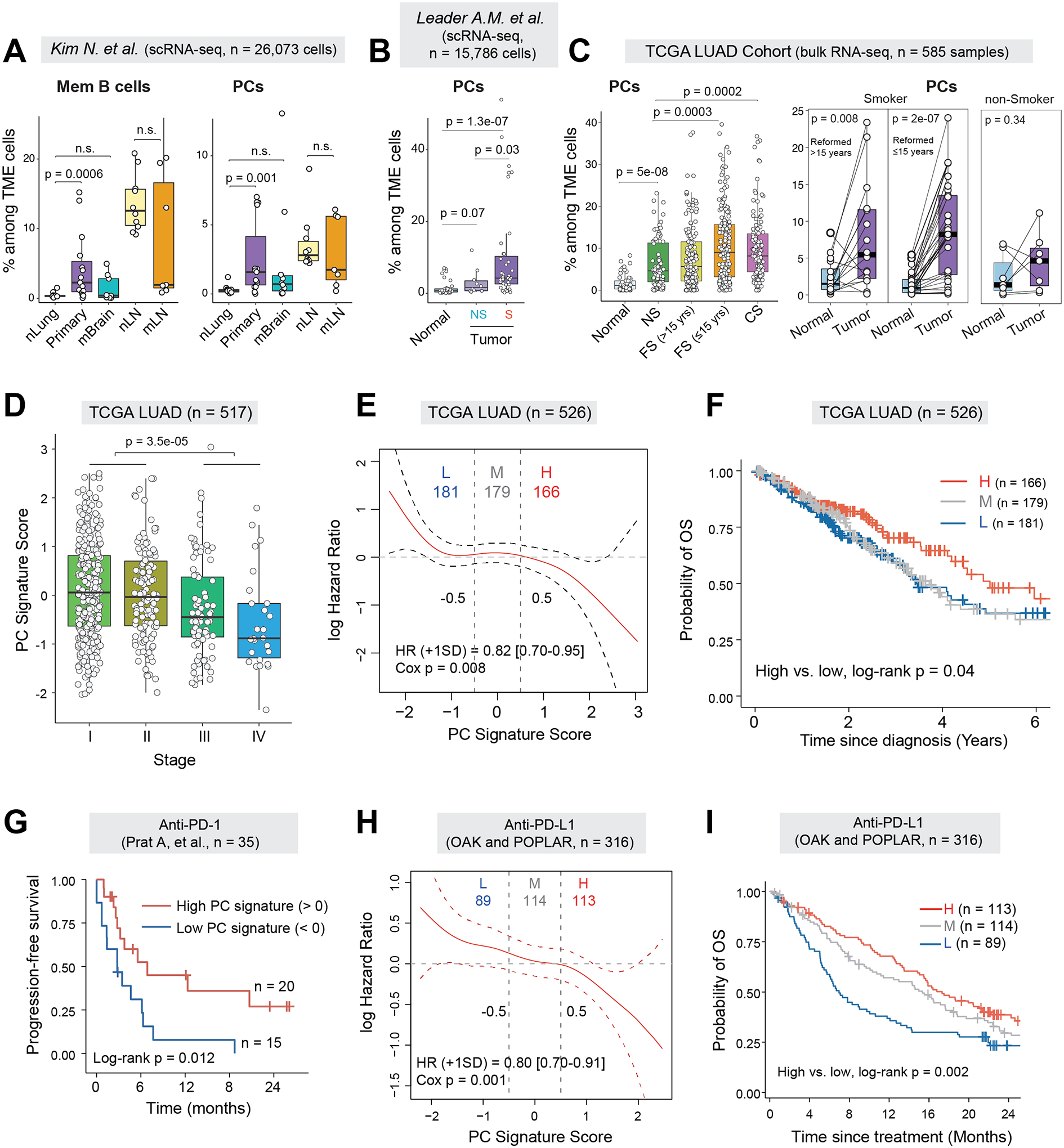
(A) Boxplots comparing cellular fractions of memory B cells (left) and plasma cells (right) among total TME cells in a public scRNA-seq dataset from Kim N. et al (10). P values were determined by Mann-Whitney tests. nLung, normal lung; Primary, primary LUAD; mBrain, brain metastases; nLN, normal lymph node (LN); mLN, lymph node metastases; n.s., not statistically significant. (B) Box plots showing the relative fractions of PCs among the TME cells in the NSCLC scRNA-seq dataset from Leader AM et.al. Only LUAD patients were included in analysis. (C) Boxplots comparing the estimated cell fractions of PCs between tumor and normal lung tissues from the TCGA LUAD cohort (left) and in a subset of patients with tumor-normal pairs (n = 52) (right). Samples were stratified by patient smoking status. NS, non-smoker; FS, former smoker; CS, current smoker. (D) Boxplot showing the expression of PC signature scores across different pathological stages of LUAD in the TCGA LUAD cohort. (E) Estimates for the dependence of all-time risk of death on plasma cell abundance in tumor (expression of plasma cell signature) in TCGA LUAD cohort. The solid curve (red) was generated using the Cox proportional hazards model and the dotted curves indicate the 95% CI of log hazard ratio. (F) Kaplan-Meier curves displaying differences in overall survival (OS) probability between TCGA LUAD patients whose tumors had high (H), medium (M) or low (L) levels of PC gene signature. (G) Kaplan-Meier curves displaying differences in progression-free survival (PFS) between patients whose pre-treatment tumors had high or low levels of PC gene signature in the Prat A et al. cohort receiving anti-PD-1 treatment (14). (H) Estimates for the dependence of all-time risk of death on plasma cell abundance in tumor of combined cohorts of OAK and POPLAR receiving anti-PD-L1 treatment. The solid curve (red) was generated using the Cox proportional hazards model and the dotted curves indicate the 95% CI of log hazard ratio. (I) Kaplan-Meier curves displaying differences in OS probability between anti-PD-L1 treated patients whose pre-treatment tumors had high, medium and low levels of PC gene signature in the combined cohorts.
