FIGURE 2.
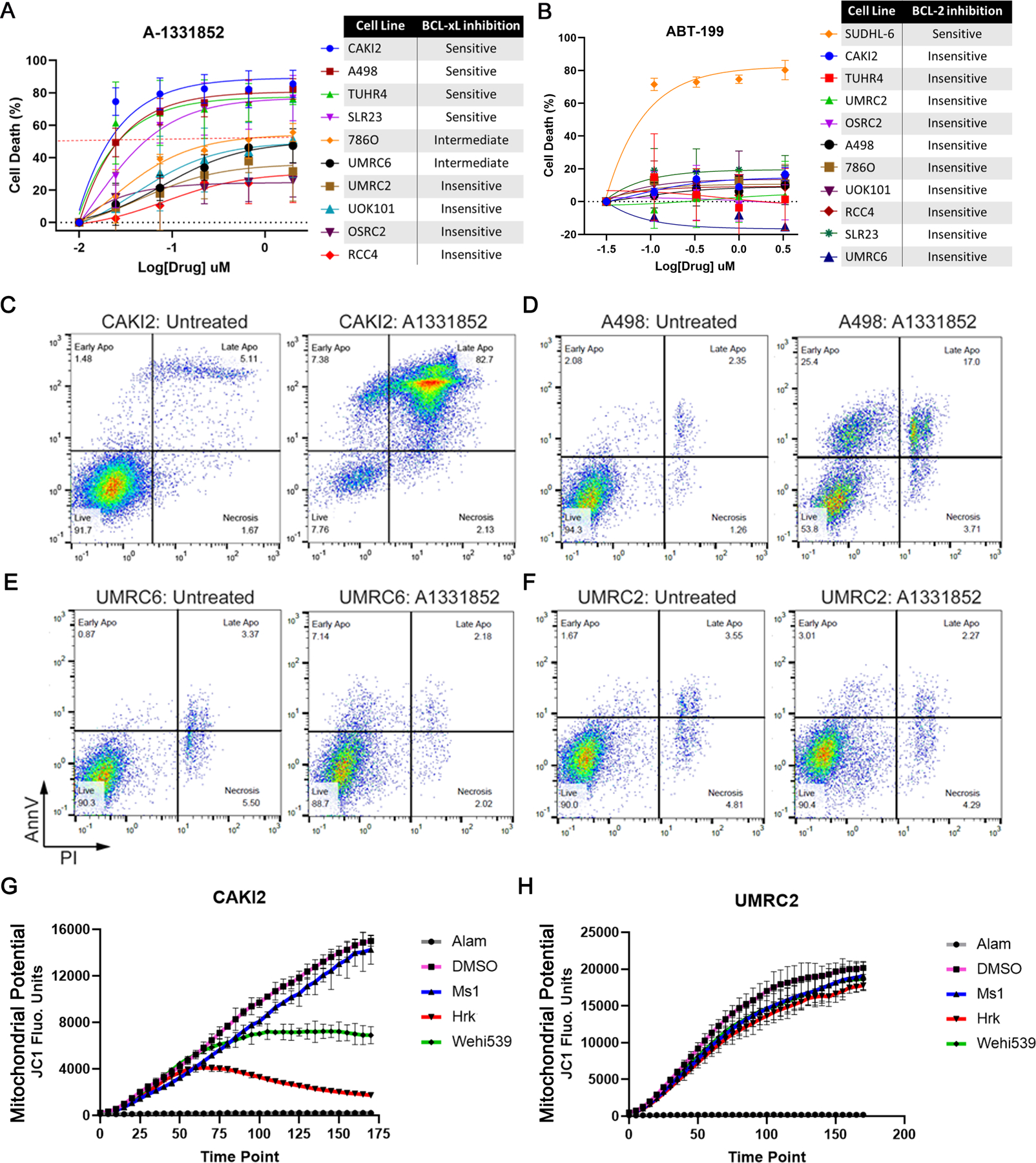
BCL-XL Inhibition Promotes Apoptotic Cell Death in a Subset of ccRCCs. Percent cell death, relative to the DMSO-treated control cells, determined using the XTT assay in the indicated ccRCC cell lines that were treated with the indicated concentrations of the BCL-XL inhibitor A-1331852 (A) or the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 (B) for 3 days. Flow cytometric analysis to compare AnnexinV-FITC (AnnV) versus Propidium Iodide (PI) staining in CAKI-2 (C), A-498 (D), UMRC-6 (E), and UMRC-2 (F) cells that were treated with A-1331852 or DMSO (Untreated control), as indicated. In (C) cells were treated with 10 nM A-1331852 for 16 hours; whereas, in (D), (E), and (F) cells were treated with 100 nM A-1331852 for 36 hours. JC1 fluorescence measurement at the indicated time-points in CAKI-2 (G) and UMRC-2 cells (H) that were exposed to Alamethicin (Alam) (positive control), DMSO (negative control), sensitizer BH3 peptides [MS1 (30 µM) targeting MCL-1 and Hrk (100 µM) targeting BCL-XL], or the small molecule BCL-XL inhibitor Wehi539 (1 µM).
