Fig. 5. Seventeen structurally-distinct derivatives were prepared and evaluated against a panel of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
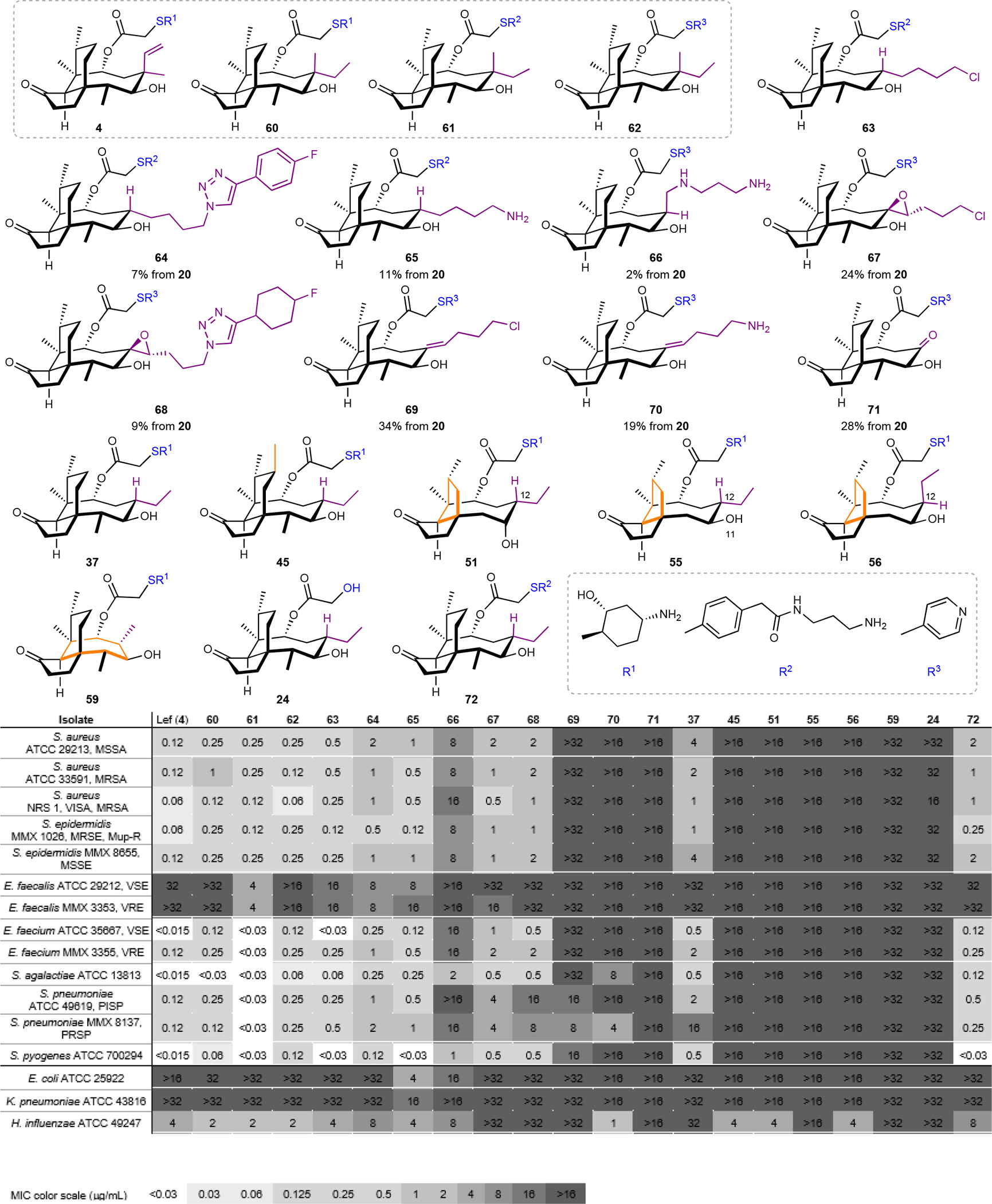
Fully synthetic pleuromutilins prepared using the synthetic platform that feature different core modifications (24, 37, 45, 63–72), ring sizes (51, 55, 56, 59) and C14 glycolic ester derivatives (R1–R3). The compounds were compared to semisynthetic controls (lefamulin (4), 60–62; shown in the gray box) against a panel of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (μg/mL) are reported. MSSA: methicillin-susceptible S. aureus; MRSA: methicillin-resistant S. aureus; MRSE: methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis; MSSE: methicillin-susceptible S. epidermidis; VSE: vancomycin-susceptible Enterococcus; VRE: vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus; PISP: penicillin-intermediate S. pneumoniae; PRSP: penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae.
