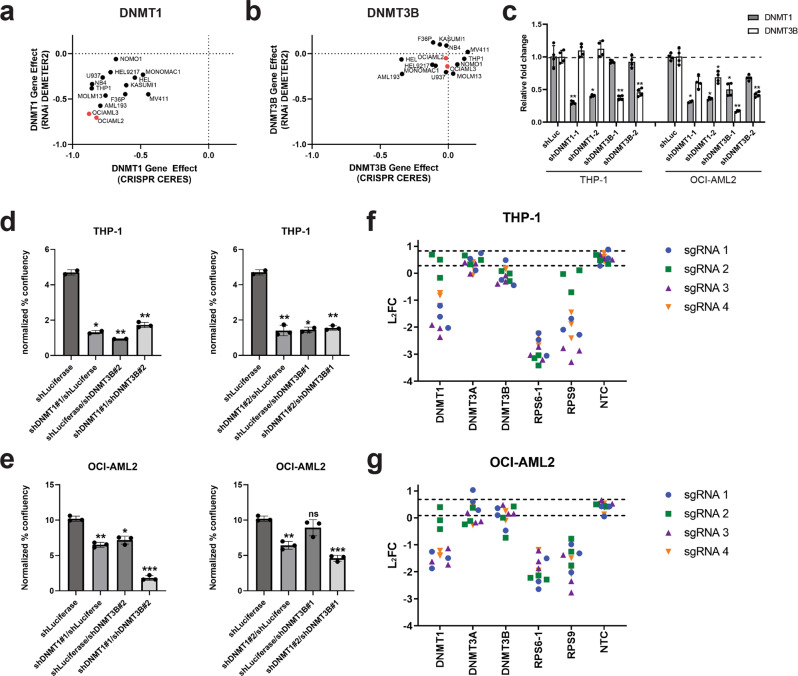
Fig. 1. Knockdown and knockout of DNMT1 inhibits cell proliferation in AML cell lines independent of the mutational status of DNMT3A.
a, b RNAi DEMETER2 and CRISPR CERES scores from publicly available AML cell lines targeting DNMT1 (a) and DNMT3B (b). The DNMT3A mutant AML cell lines, OCI-AML2 and OCI-AML3, are highlighted in red. c Relative transcript levels of DNMT1 and DNMT3B in THP-1 and OCI-AML2 cells transduced with DNMT1 and/or DNMT3B shRNAs. Relative transcript levels were normalized to GAPDH and fold change was calculated relative to cells treated with a shRNA targeting luciferase (shLuc). n = 4; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Dunnet’s multiple comparison test. d, e Spheroid-like growth assays on THP-1 cells, a cell line wild-type for DNMT3A (d), and OCI-AML2 cells, which is mutant for DNMT3A (e), transduced with DNMT1 and/or DNMT3B shRNAs. Spheroid-like cell confluence was normalized to the confluence on day 0 of the assay to calculate normalized % confluency. n = 3. *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001, ns = not significant, unpaired t-tests. f, g CRISPR/Cas9 pooled screen data for sgRNAs targeting DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B in THP-1 (f) and OCI-AML2 (g) cells. Four sgRNAs targeting each gene are shown, with experiments being performed in triplicate. RPS6 and RPS9 are common essential genes used as positive controls that affect viability. NTC are non-targeting control guides that should not affect cell growth. The dashed lines represent the mean L2FC +/−2 standard deviations (S.D.) of the non-targeting control sgRNAs included in the library.