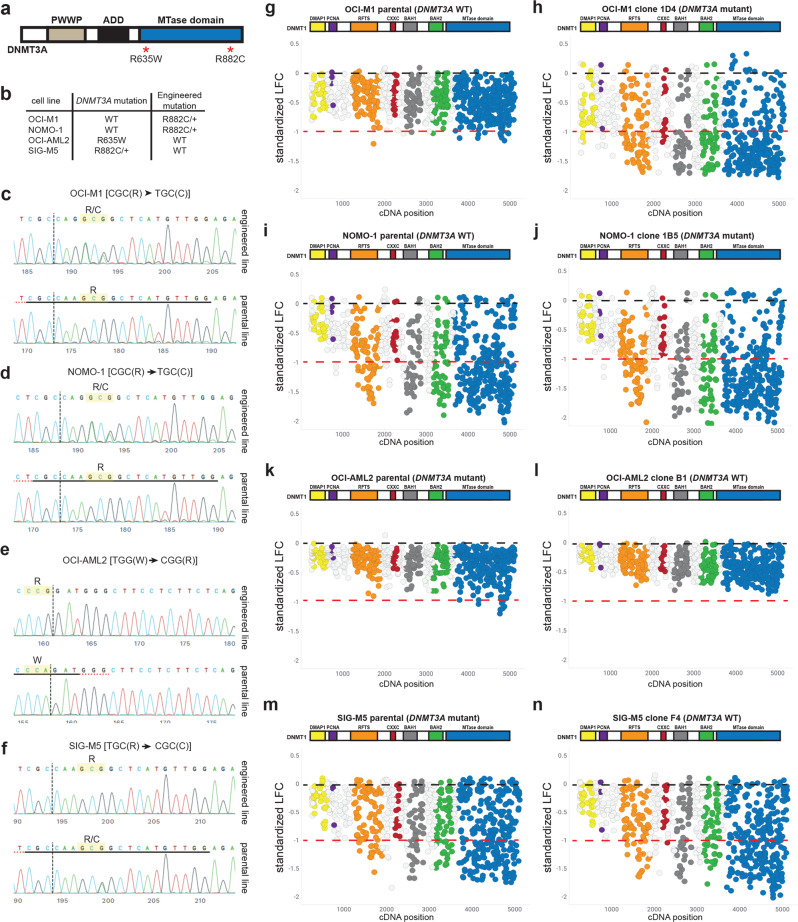
Fig. 6. Knockout mutations across the DNMT1 protein exhibit differential sensitivity across isogenic AML cell lines wild-type or mutant for DNMT3A.
a Domain architecture of the DNMT3A protein. The R882C/+ and R635W mutations in the MTase domain of DNMT3A are labeled. b The R882C/+ clinically relevant DNMT3A mutation was incorporated into OCI-M1 and NOMO-1 cells, which are normally wild-type for DNMT3A. OCI-AML2 cells, which harbor a homozygous R635W mutation in DNMT3A, were engineered to express wild-type DNMT3A. SIG-M5 cells, which harbor a heterozygous R882C mutation in DNMT3A, were engineered to express wild-type DNMT3A. c–f Sanger sequencing of the DNMT3A gene verifying the engineered mutation in OCI-M1 (c), NOMO-1 (d), OCI-AML2 (e), and SIG-M5 (f) cells. Sanger sequencing of the control parental pool of cells (bottom row), as well as the engineered clone (top row), is shown for each cell line. sgRNAs tiling DNMT1 are shown with respect to their cDNA position in OCI-M1 parental (DNMT3A WT, g and OCI-M1 DNMT3A[R882C/+] (DNMT3A mutant, h) cells. i, j sgRNAs tiling DNMT1 are shown with respect to their cDNA position in NOMO-1 parental (DNMT3A WT, i) and NOMO-1 DNMT3A[R882C/+] (DNMT3A mutant, j) cells. k, l sgRNAs tiling DNMT1 are shown with respect to their cDNA position in OCI-AML2 parental (DNMT3A mutant, k) and OCI-AML2 DNMT3A[W635R] (DNMT3A WT, l) cells. m, n sgRNAs tiling DNMT1 are shown with respect to their cDNA position in SIG-M5 parental (DNMT3A mutant, m) and SIG-M5 DNMT3A[C882R/+] (DNMT3A WT, n) cells. Black dashed line denotes the mean standardized LFC of the non-targeting controls. The mean standardized LFC of the common essential sgRNAs is denoted by the red dashed line. The color of each circle represents the functional domain it targets: DMAP1 (yellow); PCNA (purple); RFTS (orange); CXXC (red); BAH1 (dark gray); BAH2 (green); MTase domain (blue). n = 3 replicates for each screen.