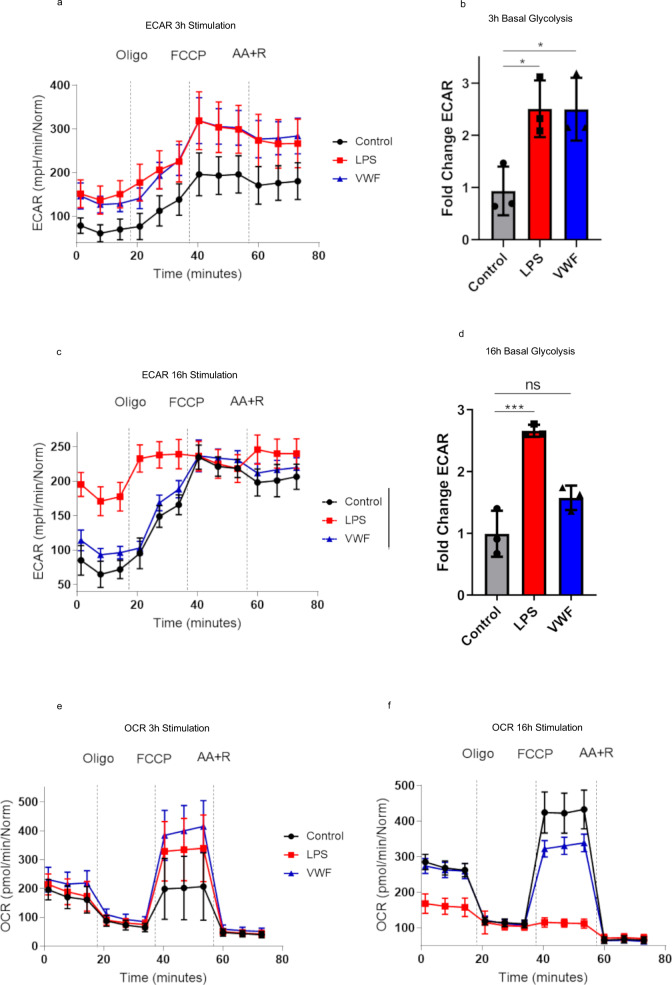
Fig. 5. VWF regulates macrophage metabolism and drives glycolysis.
Extracellular flux analysis (Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress kit) was used to assess the effects of VWF-binding upon macrophage metabolism. Extracellular acidification (ECAR) was measured to study the effects on glycolysis following stimulation with VWF (10 μg/ml) (blue), LPS (100 ng/ml) (red), or untreated controls (black) for 3 h (a, b) and 16 h (c, d) respectively. Similarly, cellular oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was assayed to study the effects on BMDM oxidative phosphorylation after 3 h and 16 h (e, f) incubations. The effects of VWF and LPS on BMDM glycolysis (*P = 0.0272 and ***P = 0.0004 for control vs LPS; *P = 0.0279 and P = 0.0646 for control vs VWF, following 3 and 16 h respectively) and oxidative phosphorylation were studied in the presence or absence of specific mitochondrial inhibitors. Plots are representative images collected from three independent assays. The data are presented as the mean values ± SD for three independent experiments. Significance was determined by ANOVA in which **p < 0.01 and ****p < 0.0001. Source data for this figure are provided as a Source Data file.