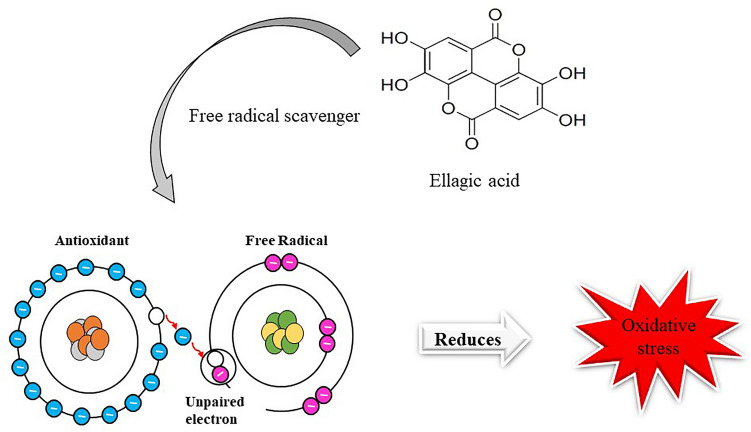
Fig. 2.
represents the mechanism of action of ellagic acid. The hydroxyl group present in the compound is responsible for scavenging the free radicals. Ellagic acid scavenges the free electrons present in the last orbital shell and therefore acts as a potent antioxidant and hence reduces the oxidative stress of the cellular components