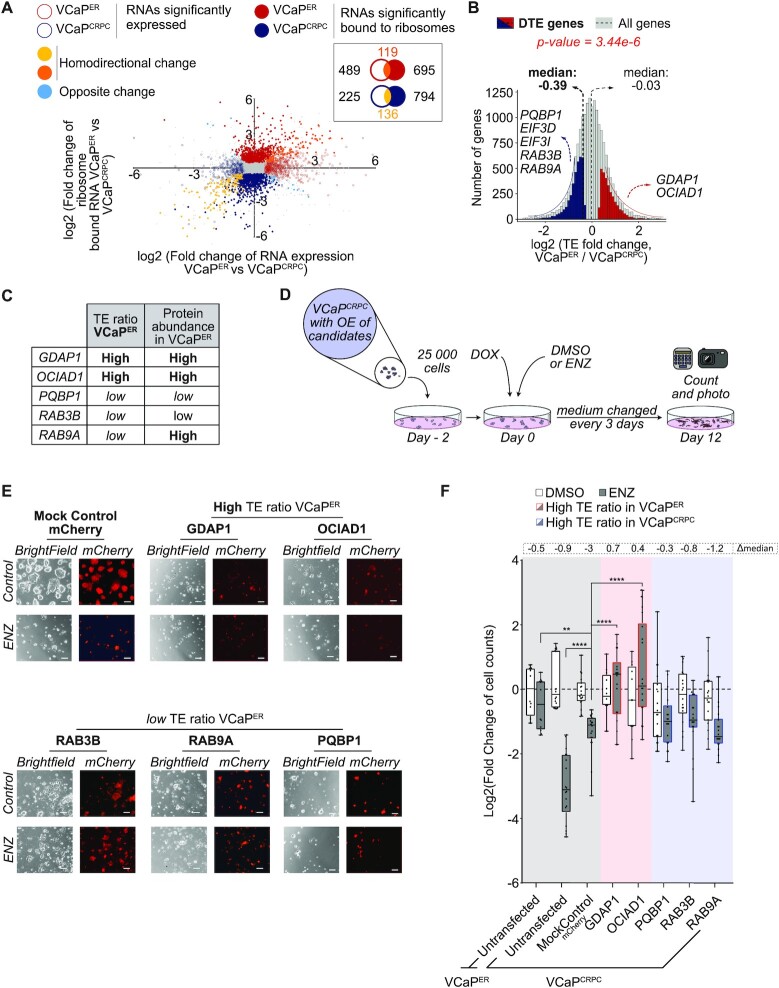
Figure 3.
Highly translated genes in VCaPER are drivers of PCa ENZ resistance. (A) Scatterplot highlighting RNAs significantly increased or decreased in the transcriptome (empty circles) or translatome (full circles) in VCaPER (red) compared to VCaPCRPC (blue). Significant genes are colored. n = 2 biological replicates for each condition. (B) TE ratios for all genes, and for genes with a significant differential TE ratio in VCaPER compared to VCaPCRPC (red for higher and blue for lower TE ratio). Medians are indicated with dashed lines (thin line for all genes, bold line for genes with significant differences in TE ratio). (C) Table of gene candidates selected for additional studies. (D) Schematic of overexpression experiments for candidate genes. (E) Representative images of cell lines for GDAP1, OCIAD1, RAB3B, RAB9A and PQBP1. Scale bar: 100 uM. (F) Fold changes of viable cell counts for cell lines overexpressing candidate genes with ENZ treatment normalized to control without ENZ treatment. Differences between ENZ-treated and control in log2(fold changes) are indicated as Δmedian. n = 2 or 3 biological replicates. *P-value < 0.05; **P-value < 0.01; ***P-value < 0.001; ****P-value < 0.0001. Only significant comparisons are shown.