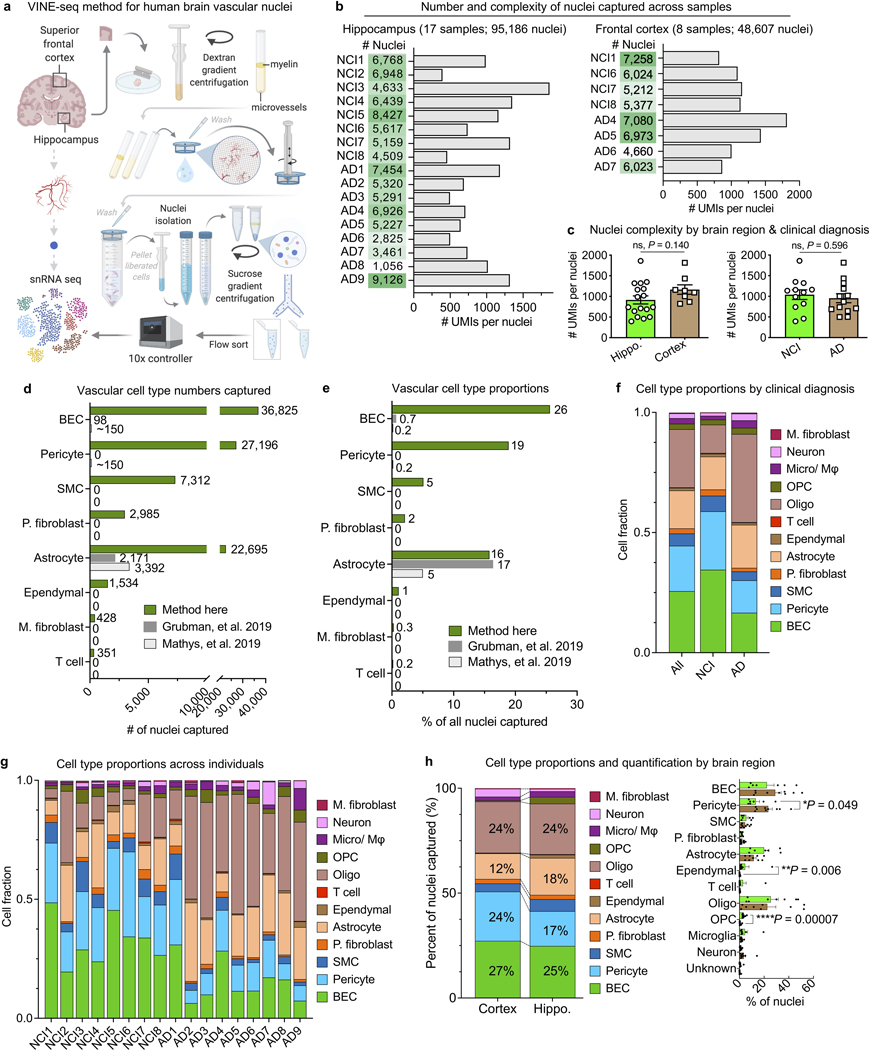
Extended Data Fig. 1. Enhanced capture and characterization of human brain vascular nuclei.
a, Detailed schematic of the VINE-seq method to capture human brain vascular and immune cell types for single-nucleus sequencing.
b, Total number of nuclei, median number of unique molecular identifiers (UMI), and median number of genes for each human sample sequenced from hippocampus and superior frontal cortex.
c, Quantification of the median number of genes detected per nuclei across subject groups (n=17 hippocampus and n=8 cortex; n=8 NCI and n=9 AD, two-sided t-test; mean +/− s.e.m.).
d, e, Quantification of the number (d) and proportion (e) of cerebrovascular cell types captured via the VINE-seq method introduced here compared to recent snRNA-seq studies16,17.
f, Summary quantification of the proportion of captured cell types by NCI and AD individuals.
g, Quantification of the proportion of captured cell types across individuals.
h, Summary (left) and quantification (right) of the proportion of captured cell types by brain region (n=17 hippocampus and n=8 cortex; n=8 NCI and n=9 AD, two-sided t-test; mean +/− s.e.m.).