FIGURE 6:
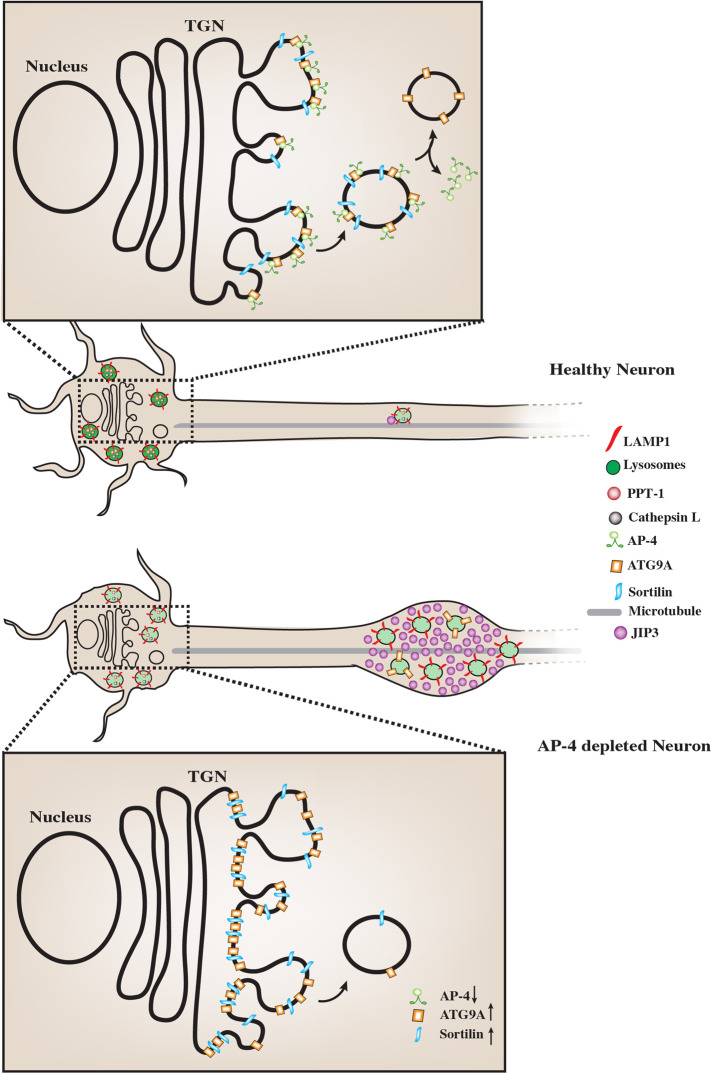
AP-4 regulates neuronal lysosome composition, function, and transport. Schematic representation of the effect of AP-4 loss on neuronal lysosome trafficking and function. In AP-4 i3Neurons there are lysosomes in the soma that contain reduced levels of certain lysosomal enzymes, such as PPT-1 and Cathepsin L. Magnified insets of the TGN area in the soma of the neurons show molecular detail of cargo potentially regulated by AP-4 action. Upon loss of AP-4 complex function, concentration and transport of Sortilin out of the TGN is affected when compared with healthy Control i3Neurons. Thus strong Sortilin accumulation in the TGN area is observed in the AP-4 i3Neurons. ATG9A, previously well-established cargo whose sorting out of the TGN is dependent on AP-4 complex function, shows a similar strong accumulation in TGN area, validating these CRISPRi-based AP-4 i3Neurons as a model for studying neuronal membrane trafficking events regulated by AP-4 complex. Also, unlike healthy Control i3Neurons, where few LAMP1-positive vesicles are observed in axons, AP-4 loss causes axonal lysosomes (LAMP1-positive vesicles) to build up in dystrophies/swellings. Additionally, there is increased accumulation of JIP3/MAPK8IP3, a regulator of retrograde axonal lysosome transport, in these swellings. We propose that the accumulation of cytosolic JIP3 in the axonal swellings in AP-4 i3Neurons could also be due to absence/reduced levels of these interacting partners on lysosomes, whose sorting from TGN to the organelle is AP-4 dependent, as with ATG9A and potentially Sortilin.