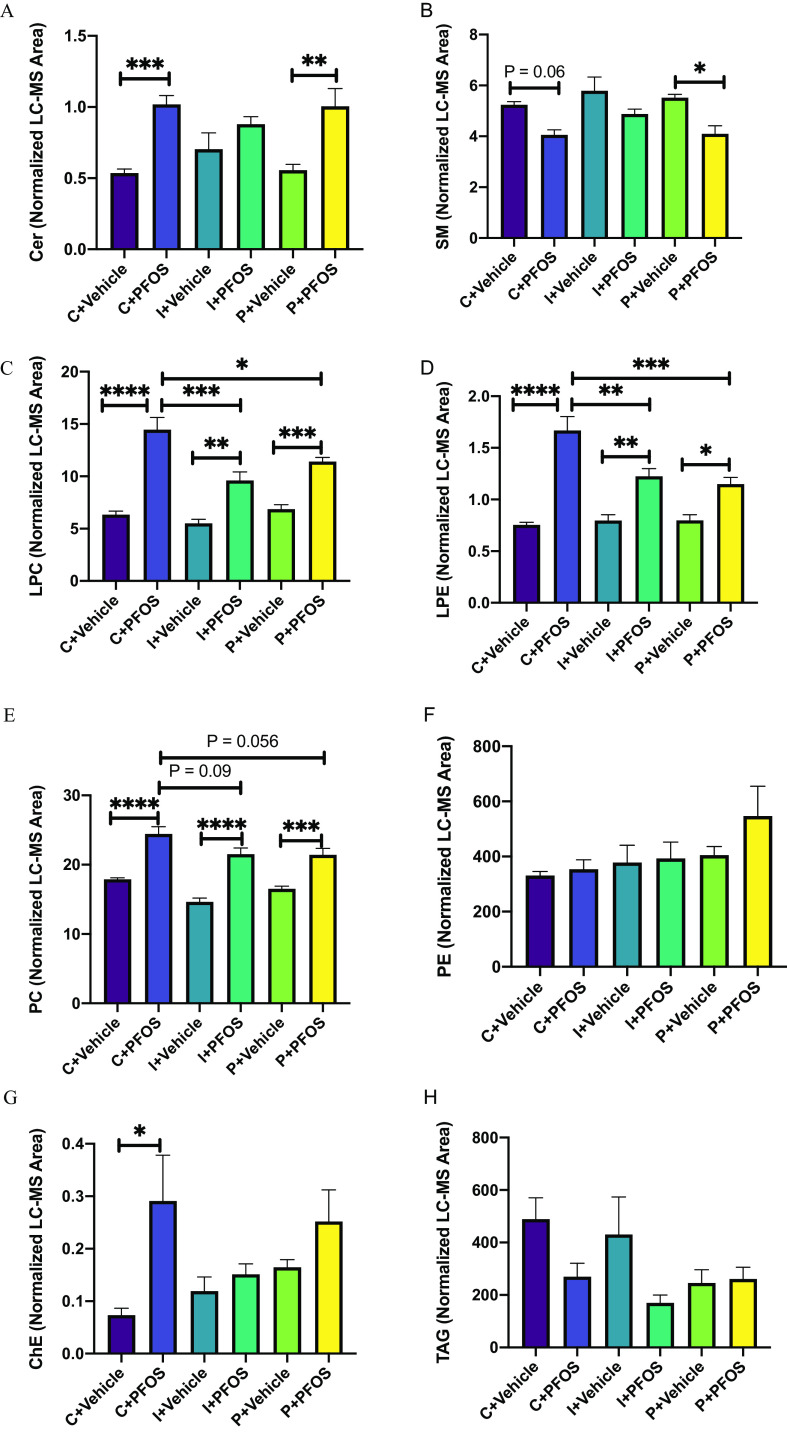
Figure 2.
Liver lipid profiles in mice exposed to PFOS and fed with diets supplemented with different fibers (C: cellulose as control, I: inulin, P: pectin). Lipids including sphingolipids (Cer, A; SM, B), lysophospholipids (LPC, C; LPE, D), phospholipids (PC, E; PE, F), cholesterol ester (ChE, G), and a neutral lipid (TAG, H) were analyzed using UHPLC-Q exactive MS. The normalized peak areas of lipid species in each lipid class are summarized. Bars represent of 6–8 mice in each group. Data were compared using two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons, *; **; ***; and ****. Detailed lipidomic data are listed in Excel Table S12. Note: ANOVA, analysis of variance; Cer, ceramide; LC-MS, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; LPE, lysophosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PFOS, perfluorooctane sulfonate; SEM, standard error of the mean; SM, sphingomyelin; UHPLC-Q exactive MS, ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-exactive mass spectrometer; TAG, triacylglycerol.