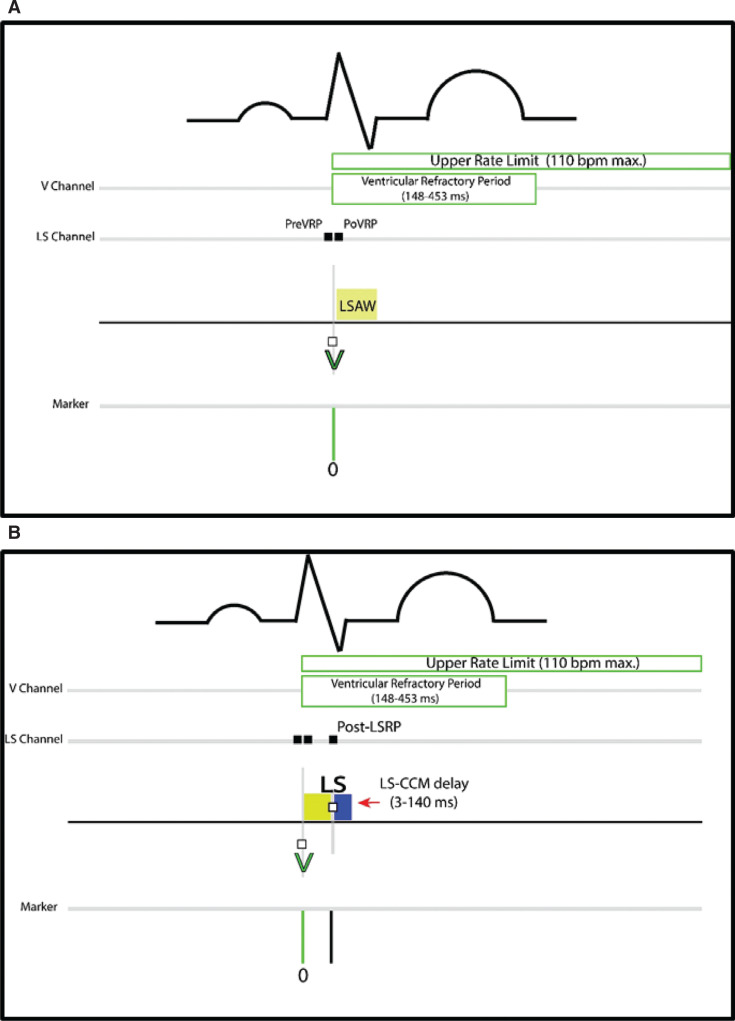
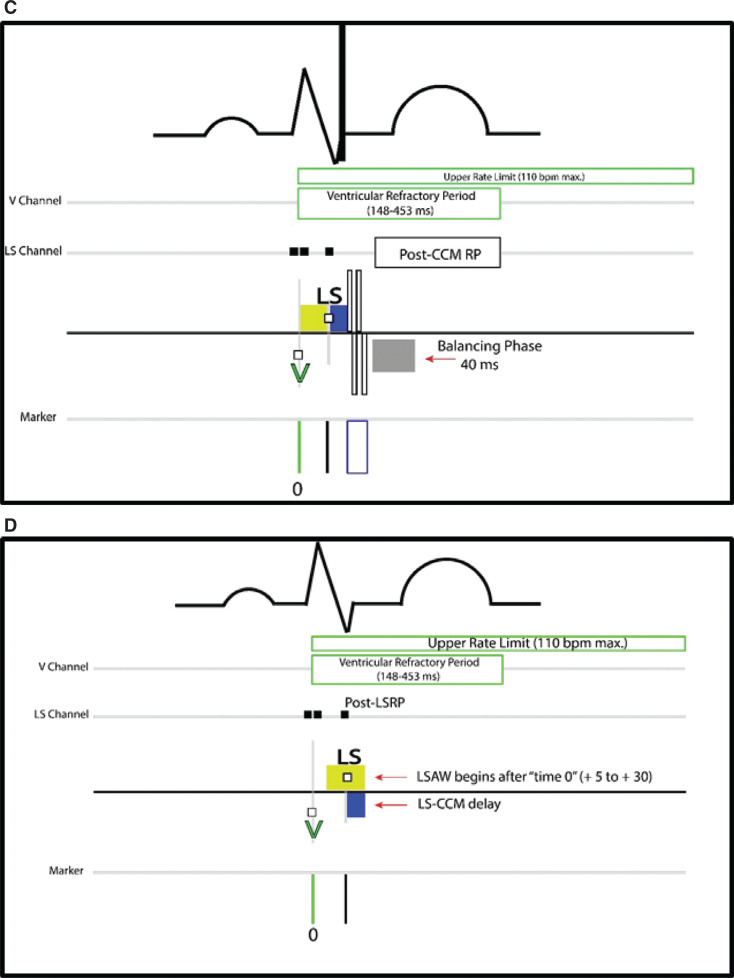
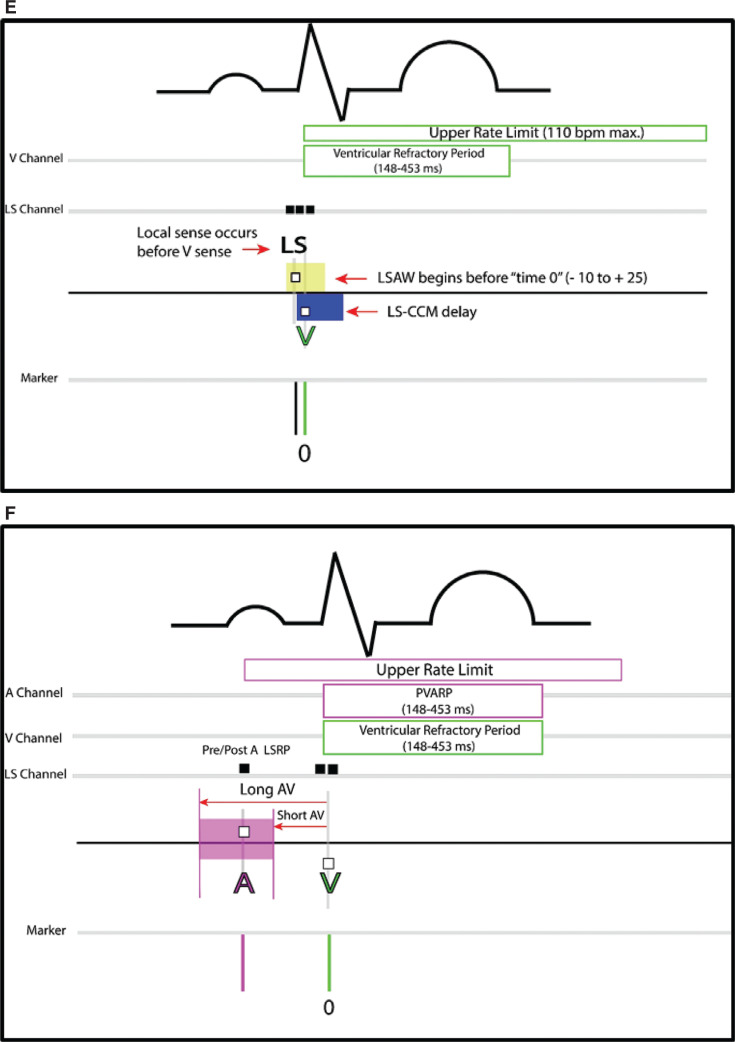
Figure 4:
Cardiac contractility modulation (CCM) timing for OVO and ODO modes. OVO mode timing is shown in panels A–E. Additional criteria for ODO function are displayed in panel F. A: A V channel sense (“time zero”) begins the process and opens the local sense alert window (LSAW). B: An LS channel sense closes the LSAW and triggers the LS-CCM delay. C: CCM therapy delivers at the end of the LS-CCM delay absent an additional LS channel sense. Normal programmed timing variants may occur with an LSAW beginning a short time after D: or before E: an RV channel sense. E: The implantable pulse generator looks back from time zero for an LS channel sense that occurs earlier in time, but within the LSAW, to trigger an LS-CCM delay. The LS-CCM delay is adjusted in both variants (D and E) to time the CCM pulse properly. F: Atrial sensing within the long and short atrioventricular windows is required after an RV channel sense to initiate the LSAW in the ODO mode. Only following atrial sensing in this window does the process continue as seen in A–C. Otherwise, CCM is not delivered for that beat. Abbreviations: A, atrial; AV, atrioventricular; CCM, cardiac contractility modulation; IPG, implantable pulse generator; LS, local sense; LSAW, local sense alert window; LS-CCM, local sense–cardiac contractility modulation; Pre A LSRP, pre-atrial local sense refractory period; Post A LSRP, post-atrial local sense refractory period; Post-CCM RP, post-cardiac contractility modulation refractory period; PreVRP, pre-ventricular refractory period; PoLSRP, post-LS refractory period; PoVRP, post-ventricular refractory period; PVARP, post-ventricular atrial refractory period; RV and V, right ventricular.