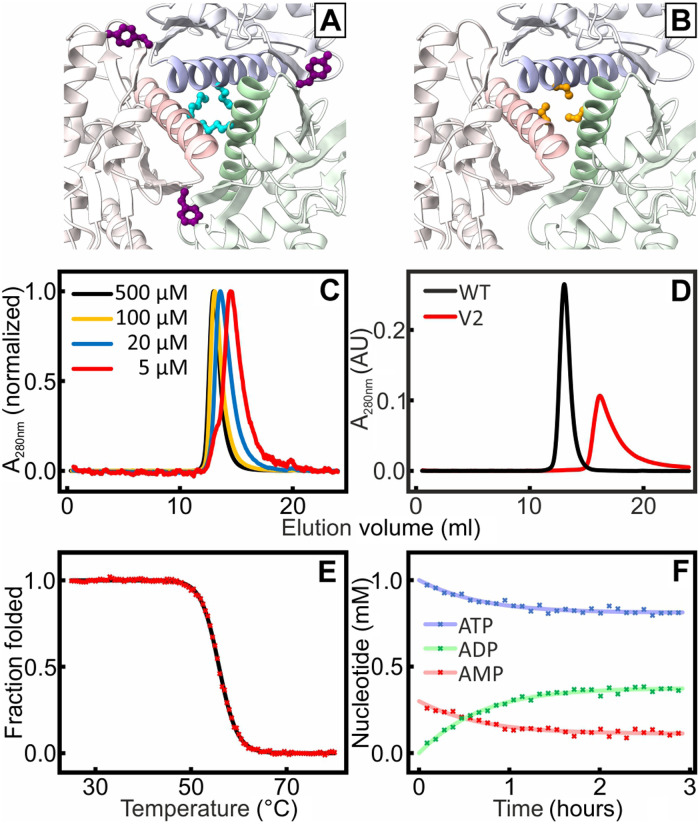
Fig. 6. Formation of monomeric OdinAK by disruption of trimerization interfaces.
The trimerization interfaces were destabilized by replacing key amino acid residues identified from structural analysis. In V1, M154 (cyan) and Y166 (purple) (A) were mutated into glutamic acid. In V2, Met154, Tyr166, and Ser158 (orange) (B) were mutated into arginines. (C) SEC of different concentration samples of V1 showed that the elution for samples with decreasing concentration samples was shifted toward higher volumes, indicating the presence of an equilibrium between different oligomeric states. (D) The SEC profile for V2 (red) indicated a fully monomeric state that elutes at a volume that is significantly larger than that of a wild-type (WT) reference trimer (black). (E) Thermal unfolding of V2 probed with CD spectroscopy at 222 nm; Tm was determined to 56°C. (F) The kcat value of monomeric V2 at 25°C is 0.5 s−1 as quantified from the 31P NMR activity assay.