Figure 4. Corticosterone facilitates ligand-mediated α1b adrenoreceptor internalization.
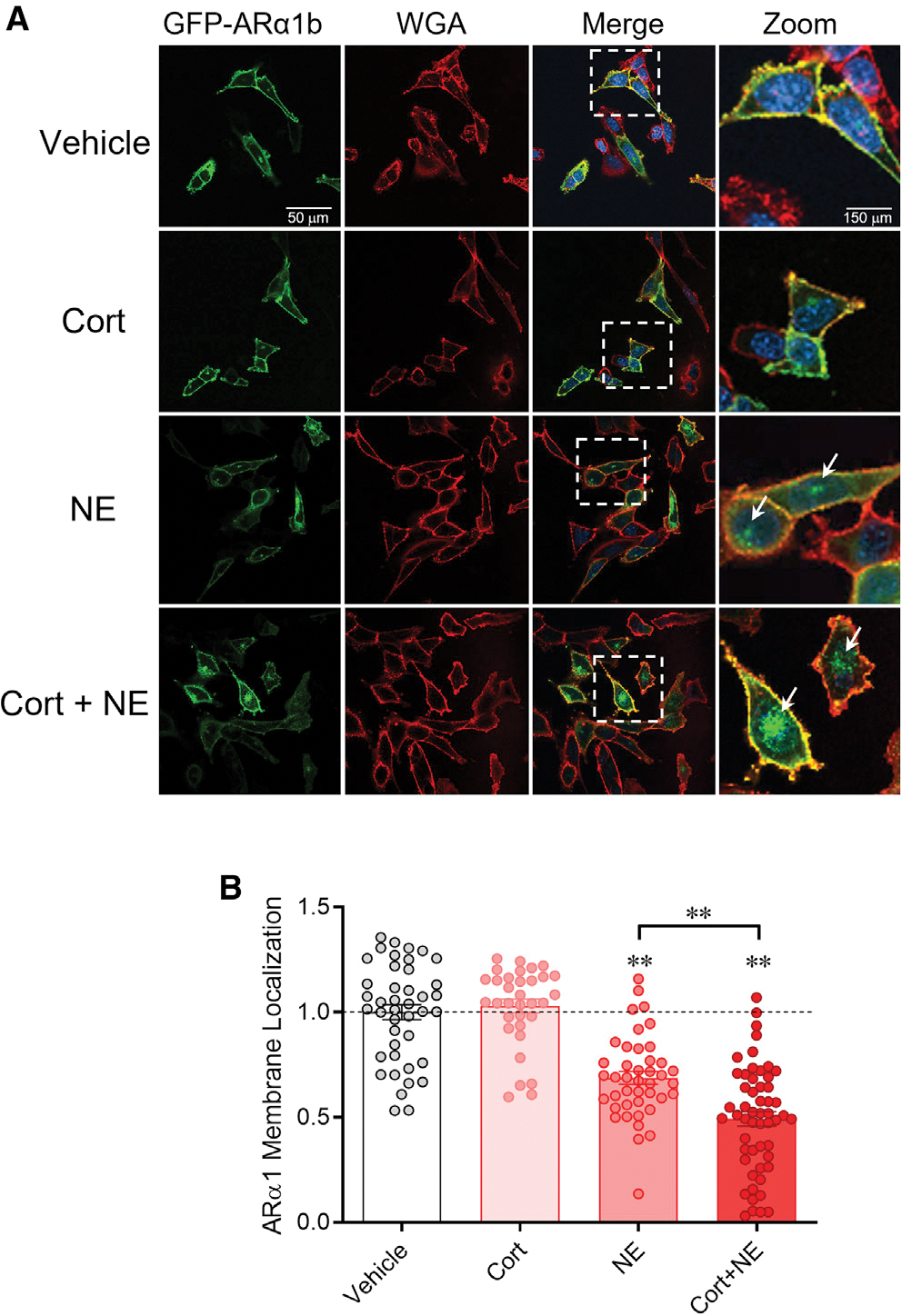
(A) Serum-stripped N42 hypothalamic cells were transiently transfected with ARα1b-eGFP (green) and co-stained with the membrane marker wheatgerm agglutinin (WGA-594, red) and the chromatin marker DAPI (blue). Vehicle: Expression of ARα1b-eGFP is localized largely in the plasma membrane under baseline conditions. Cort: ARα1b-eGFP localization is maintained in the membrane following corticosterone treatment. NE: NE treatment increased ARα1b-eGFP localization in the cells, seen as eGFP staining in intracellular “hotspots” (white arrows) and a decrease in membrane co-localization with WGA-594. Cort + NE: Co-application of corticosterone with NE increased the ARα1b-eGFP concentrated in intracellular hotspots (white arrows) and decreased ARα1b-eGFP and WGA-594 membrane co-localization.
(B) Summary of the relative ARα1b membrane localization in N42 cells in vehicle and after incubation in corticosterone alone (Cort), NE alone (NE), and corticosterone and NE (Cort + NE), normalized to vehicle. Co-localization of ARα1b-eGFP with WGA was calculated as a Pearson’s coefficient comparing pixel intensity normalized to vehicle. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01.
