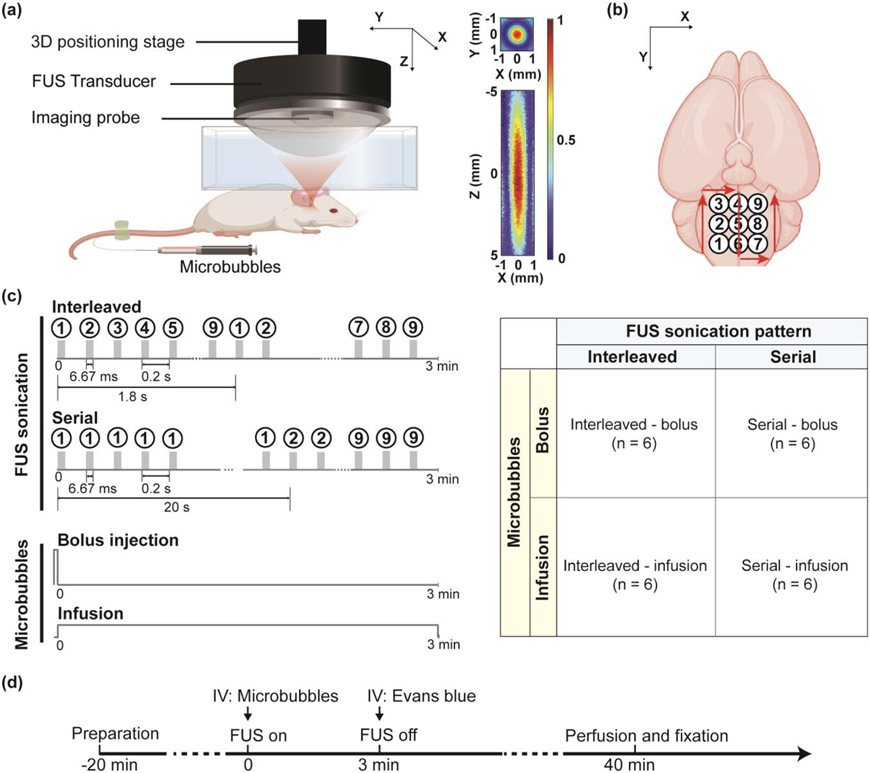
Fig. 1.
Experimental methods for comparing different strategies for large-volume FUS-BBBO. (a) FUS treatment setup. 2D pressure maps of the FUS beam in the transverse plane (XY) and axial plane (XZ) are presented to show the beam dimension. (b) FUS sonication was performed using a 3×3 grid with a spacing of 1 mm to cover the mouse brainstem. (c) Multi-point FUS sonication was performed using strategies that combined different FUS sonication patterns (interleaved vs. serial) with different microbubble injection methods (bolus vs. infusion). In interleaved sonication, each point received one pulse (10,000 cycles, 6.67 ms) per iteration of 1.8 s, leading to a total of 100 pulses during 3-min sonication. In serial sonication, each point received 100 pulses within 20 s. (d) Mouse experimental timeline. After the mouse was prepared ready, microbubbles were bolus injected or infused followed by FUS sonication using different sonication patterns. Immediately after FUS sonication, a model drug, Evans blue was injected intravenously (IV). At 40 min after FUS sonication, the animal was sacrificed for quantification of the drug delivery outcome.