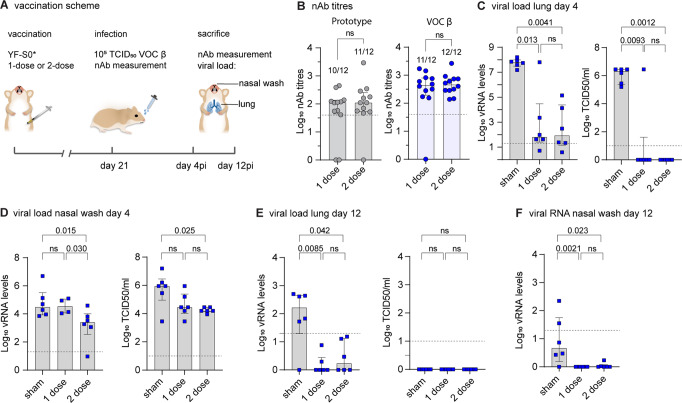
Fig. 3. Protection by YF-S0* against vigorous high-dose VOC Beta challenge.
A Vaccination scheme with updated YF-S0*. Syrian hamsters were immunized either once (n = 12) or twice (n = 12) intraperitoneally with 104 PFU of YF-S0* and n = 12 hamsters were sham vaccinated and inoculated intranasally on day 21 with 105 median tissue-culture infectious dose (TCID50) of VOC Beta. Animals were sacrificed on either day 4 (n = 18) or day 12 (n = 18) after infection (each timepoint n = 6 each per group; once or twice YF-S0* vaccinated, and sham). B nAb titres against prototypic (gray circles) and VOC Beta (blue circles) spike-pseudotyped virus on day 21 after vaccination with prototype YF-S0*. Numbers above bars indicate animals seroconverted. C–F Viral loads in hamster lungs (C, E) and nasal wash (D, F) 4 (C, D), or 12 (E, F) days after infection quantified by quantitative PCR with reverse transcription (RT-qPCR) and virus titration (blue squares). RNA extracts from 1-dose sample from 2/6 animals were not available to analyze viral RNA levels (D). Bar graphs denote median ± IQR. Dashed line represents the lower limit of quantification. Differences between groups were analyzed using nonparametric two-tailed Mann–Whitney (B) or Kruskal–Wallis test uncorrected for ties (C–F).