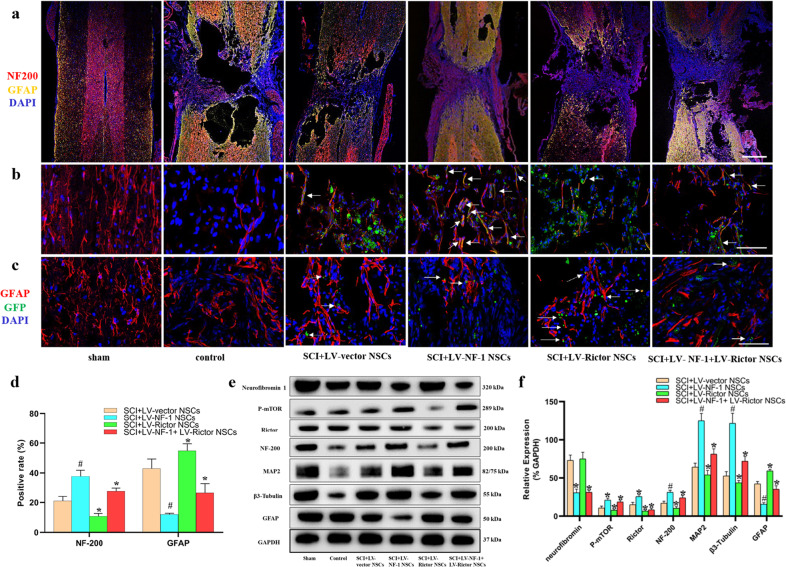
Fig. 5. Knockout of NF-1 improved neuronal differentiation and enhanced the mTORC2 pathway in transplanted neural stem cells (NSCs) in vivo.
a Tile scan images of spinal cord injury with immunofluorescence staining of neural markers (NF-200 and GFAP) (scale bar = 500 µm). b, c Immunofluorescence staining of green fluorescent protein (GFP), neurofilament outgrowth marker (NF-200), and astrocyte marker (GFAP) (scale bar = 100 µm). d Quantitative comparisons (positive rates) of NF-200- and GFAP-positive cells in different groups. e Western blotting of mTORC2 signaling pathway-related proteins (neurofibromin, P-mTOR, and Rictor), neural differentiation proteins (NF-200, MAP2, β3-Tubulin, and GFAP), and GAPDH. f Quantitative comparisons of the expression levels of neurofibromin, P-mTOR, Rictor, NF-200, MAP2, β3-Tubulin, and GFAP in different groups (data are expressed relative to GAPDH). *P < 0.05 compared with the SCI+LV-vector NSC group; #P < 0.05 compared with the SCI+LV-NF-1+LV-Rictor NSC group.