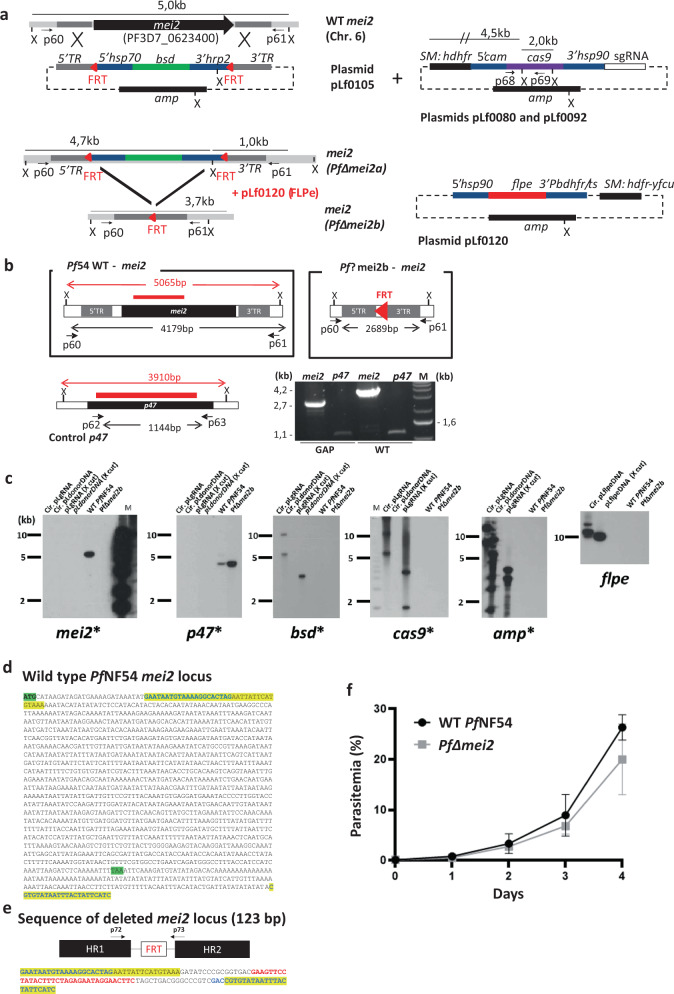
Fig. 1. Generation, genotyping, and blood-stage growth of PfΔmei2 (LA-GAP, GA2).
a Left: the mei2 (PF3D7_ 0623400) genomic locus on chromosome 6 (Chr. 6) of wild-type Pf NF54 (WT Pf NF54) and PfΔmei2 parasites before (PfΔmei2a) and after (PfΔmei2b) FLPe-mediated removal of the blasticidin-S-deaminase (bsd) selectable marker (SM). The donor plasmid pLf0105 to delete mei2 contains the bsd SM, flanked by two frt sites (red triangles) and mei2 targeting sequences (5′ TR and 3′ TR) for double cross-over integration. Primer pairs p60/p61 and PCR fragment size for diagnostic PCR are indicated (b); X (XmnI): restriction site used for Southern blot analyses (c). hsp70, heat shock protein 90; hrp2, histidine-rich protein II; amp, ampicillin. Right top: sgRNA plasmids (pLf0080, pLf0092) containing the human dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase (hdhfr) SM and the cas9 expression cassette. Cam, calmodulin. PCR primers (p68/p69) to amplify part of cas9, sizes of the sgRNA constructs after XmnI (X) digestion and mei2 and cas9 probes are indicated (c). Right bottom: construct pLf0120 with the hdhfr-yfcu SM and the flpe expression cassette. pbdhfr/ts,: P. berghei bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase, putative. See Supplementary Table 1 for primers details. b WT Pf NF54 and PfΔmei2b genomic loci and the control gene p47 (coding sequence shown as black boxes). Shown are the 5′ and 3′ mei2 targeting regions (5′TR and 3′TR), used construct pLf0105 (a) and the frt site. PCR primers (in black) for amplifying mei2 (p60/p61) and p47 (p62/63), expected sizes of the full length mei2 and p47 genes and size of mei2 locus after mei2 deletion and removal of bsd SM cassette are shown. X (XmnI): restriction site used for Southern analysis (c). DNA probes used in Southern analyses (c) and sizes of digested DNA fragments recognized by the probes (mei2 and p47) are shown (in red). Red triangle: the 34 bp frt site in the PfΔmei2b genome after removal of the bsd SM cassette. PCR (right lower panel) analysis of WT Pf NF54 and PfΔmei2b genomic DNA confirms mei2 deletion (control: amplification of p47). Primer pairs: p60/61 for mei2 and p62/p63 for p47. See Supplementary Table 1 for primer details). M, molecular weight marker; 1 kb DNA ladder (Invitrogen). c Southern analysis of restricted genomic DNA from WT Pf NF54, PfΔmei2b, and plasmids used to delete mei2 (DNA digested with XmnI (X)). DNA-samples/lanes: (i) circular sgRNA plasmids (Cir.pLgRNA); (ii) circular donor DNA plasmid pLf0105 (pLΔmei2); (iii) XmnI-digested sgRNA plasmid (pLgRNA-X cut); (iv) XmnI-digested donor DNA plasmid; v) genomic WT Pf NF54 DNA; (vi) genomic PfΔmei2b DNA. Probes: part of mei2, p47 (control), cas9, bsd, amp and flpe (see a and b for probe location and expected fragment sizes). Hybridizations show correct mei2 deletion and absence of cas9, bsd, amp and flpe in PfΔmei2b. M, molecular weight marker; 1 kb DNA ladder (Invitrogen) labeled on the sides of the gels. d Sequence of the WT PfNF54 mei2 locus. Yellow: sequences present in the disrupted mei2 locus of PfΔmei2 (e); Green: start and stop codon of mei2. e The mei2 locus in the PfΔmei2 genome after mei2 deletion by integration of pLf0105 and FLPe-mediated removal of the bsd SM marker The mei2 targeting regions (HR1 and HR2) for double cross-over integration and the frt site are shown. In addition, the sequence of the PCR fragment of the mei2 locus is shown, amplified using primers p72/p73 (see Supplementary Table 1 for primer details). Yellow: sequences present in the mei2 locus of WT PfNF54 and PfΔmei2. Red: the 34 bp FRT sequence, flanked by 16 bp and 14 bp cloning restriction sites. f In vitro growth rate of PfΔmei2 and WT Pf NF154 asexual blood stages. Parasitemia (%) during a 4-day culture period (mean and s.d. of three cultures). Error bars represent standard deviation.