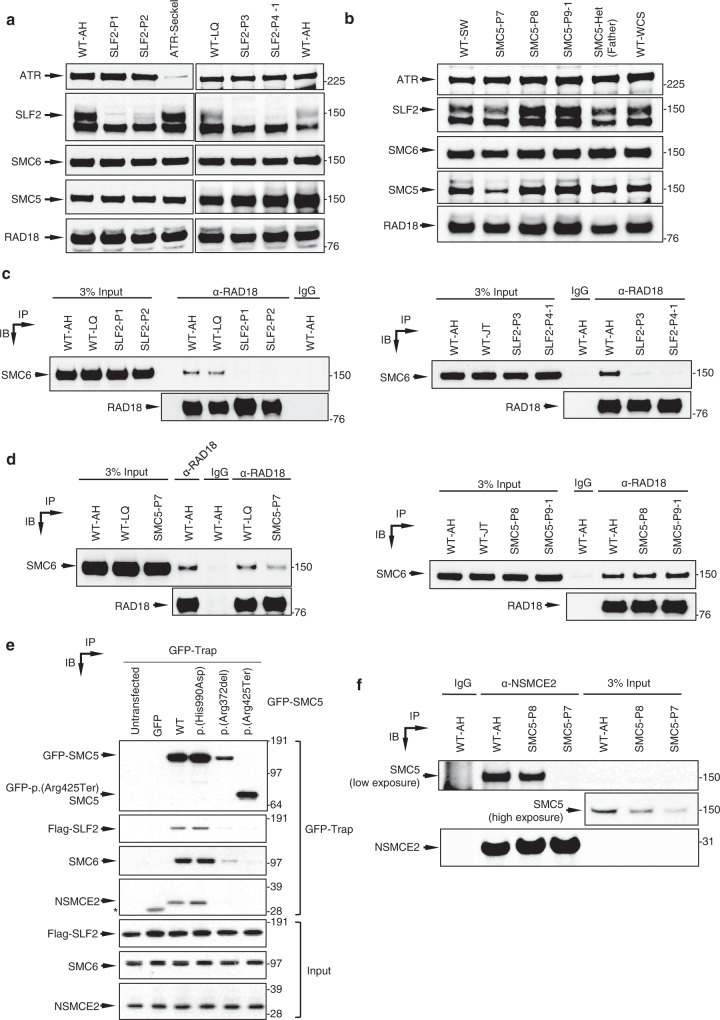
Fig. 2. Impact of patient-associated variants on the stability of SLF2 and SMC5 protein and the integrity of the SMC5/6 complex.
a Representative immunoblot analysis of cell extracts from lymphoblastoid (LCL) cell lines derived from patients with variants in SLF2. WT-AH and WT-LQ (WT wild type) indicate unrelated heathy individuals. b Representative immunoblot analysis of cell extracts from LCLs derived from patients with variants in SMC5. WT-SW and WT-WCS indicate unrelated heathy individuals. c, d Whole-cell extracts prepared from WT cell lines, SLF2 patient LCLs (c) or SMC5 patient LCLs (d) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibodies, and inputs and immunoprecipitates (IP) were analysed by immunoblotting (IB). e U-2 OS cells expressing Flag-SLF2 were transfected with WT or mutant GFP-SMC5. GFP-SMC5 was precipitated from cell extracts using GFP-Trap beads and co-precipitated proteins were detected using immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. *represents a cross-reaction of the NSMCE2 antibody to GFP. f Whole-cell extracts prepared from WT cell lines or SMC5 patient LCLs were subjected to immunoprecipitation with the indicated antibody, and inputs and immunoprecipitates were analysed by immunoblotting. Immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation experiments in (a, b, c, d, f) are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. Panel e is representative of three independent experiments with similar results.