Figure 3. Effect of size and folding mechanism on protein folding rates.
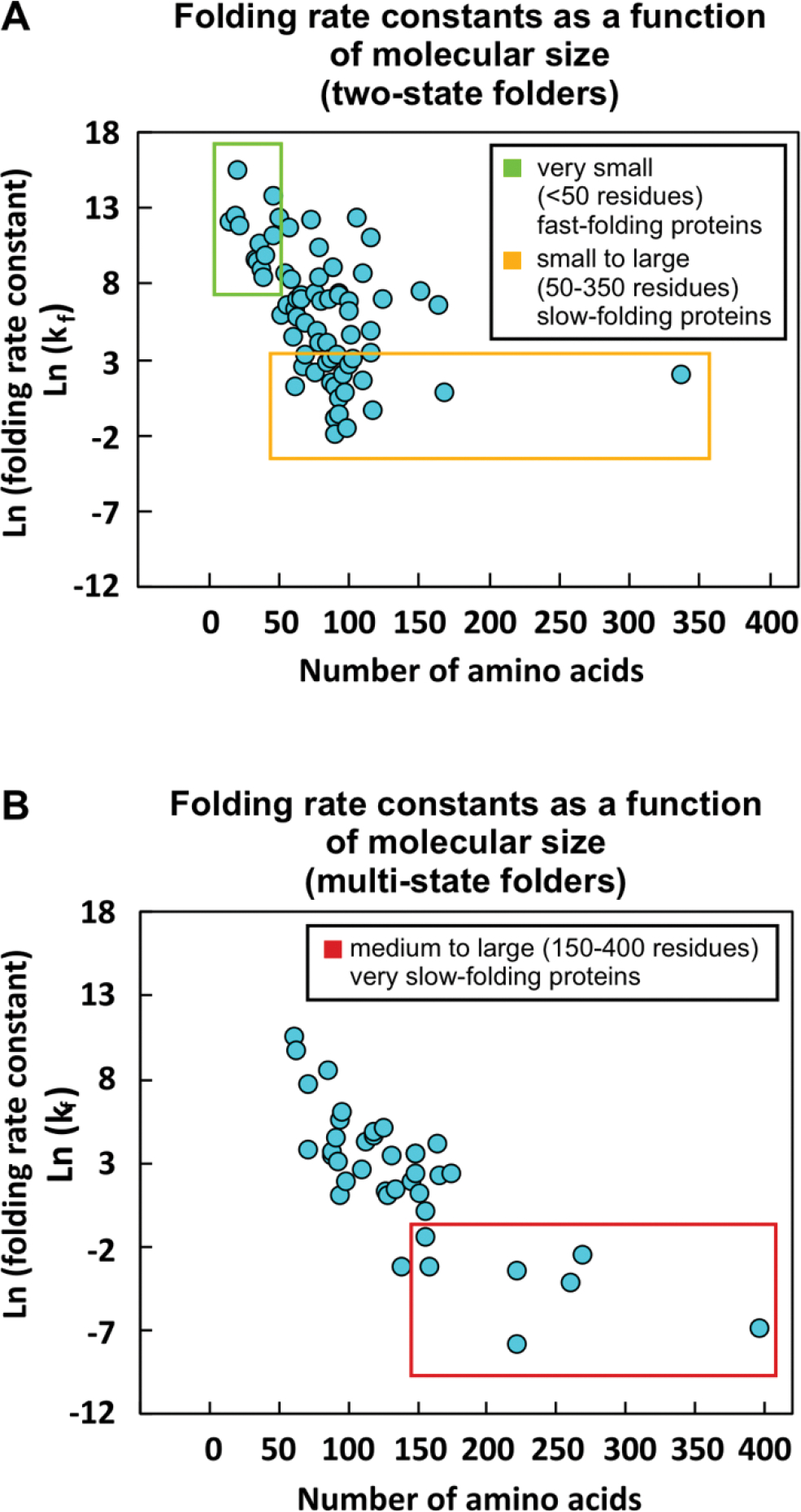
(A) Plot illustrating the dependence of protein folding rate constant (kf) on the number of residues for two-state folding proteins. Small (<50 residues) two-state proteins fold quickly with ln(kf) > 9.4 (green box). Many larger two-state folders fold more slowly (orange box). (B) Dependence of protein folding rate constant (kf) on the number of residues for multi-state folding proteins. Large (>200 residues) multi-state proteins have the slowest folding rates, with ln(kf) <−2.5 (red box). A list of the proteins and references for the data in this plot is available as Supplementary Information Table S1.
