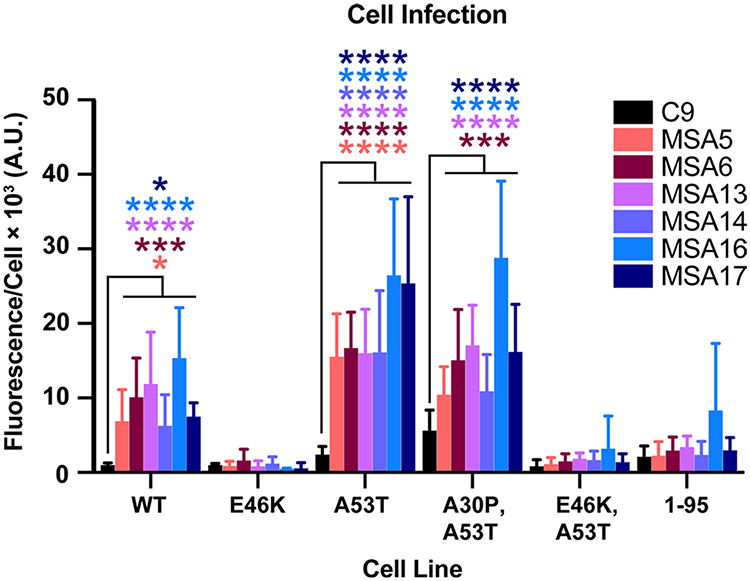
Fig. 3.
MSA patient samples transmit α-synuclein prions to TgM20+/− mice. Eight-week-old TgM20+/− mice were inoculated with 30 μL of control patient sample (C9) or six different MSA patient samples (MSA5, MSA6, MSA13, MSA14, MSA16, and MSA17). Brain homogenates from inoculated TgM20+/− mice were assessed for α-synuclein prion transmission using our cell-based assay [35, 39]. α-Synuclein prions were isolated via phosphotungstic acid precipitation and were incubated with α-syn–YFP cells for 4 d. The cell lines tested express wild-type (WT) α-syn–YFP, single mutations (E46K and A53T), double mutations (A30P,A53T and E46K,A53T), or A53T truncated at residue 95 (1–95). None of the homogenates from C9-inoculated TgM20+/− mice infected the cells, but MSA-inoculated mouse samples infected WT, A53T, and A30P,A53T cells (* = P < 0.05; *** = P < 0.001; **** = P < 0.0001)