Fig. 5.
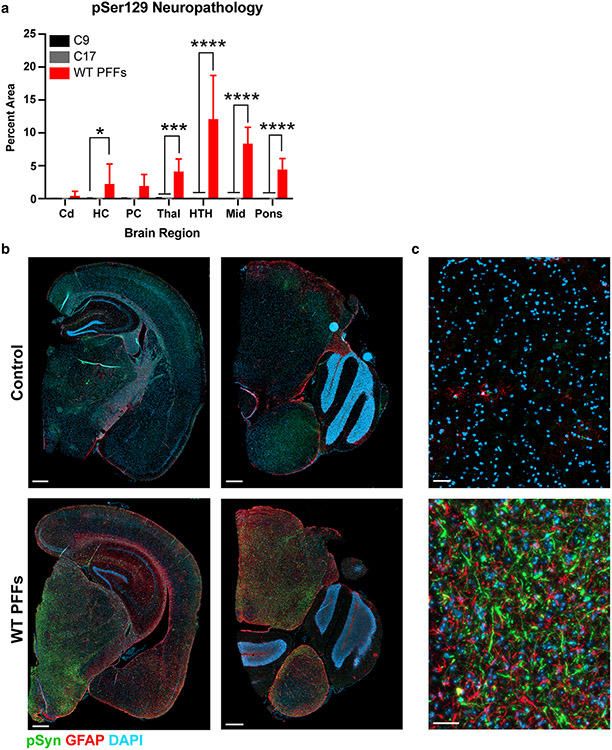
WT PFFs induce robust phosphorylated α-synuclein pathology in terminal TgM20+/− mice. Eight-week-old TgM20+/− mice were inoculated with either 30 μL of two control patient samples (C9 and C17) or 30 μg of WT PFFs. a Quantification of stained brain slices showed no phosphorylated α-synuclein inclusions were present in the caudate (Cd), hippocampus (HC), piriform cortex and amygdala (PC), thalamus (Thal), hypothalamus (HTH), midbrain (Mid), or pons of control-inoculated mice. However, WT PFFs induced robust neuropathological lesions in the HC, Thal, HTH, Mid, and pons (* = P < 0.05; *** = P < 0.001; **** = P < 0.0001). b, c Representative images from either C9-inoculated (top row) or WT PFF-inoculated mice (bottom row). Phosphorylated α-synuclein in green, GFAP in red, and DAPI in blue. b Images on the left include the HC, PC, Thal, and HTH. Images on the right include the pons and a portion of the cerebellum. Scale bar: 500 μm. c Higher magnification of Mid α-synuclein neuropathology. Scale bar: 50 μm