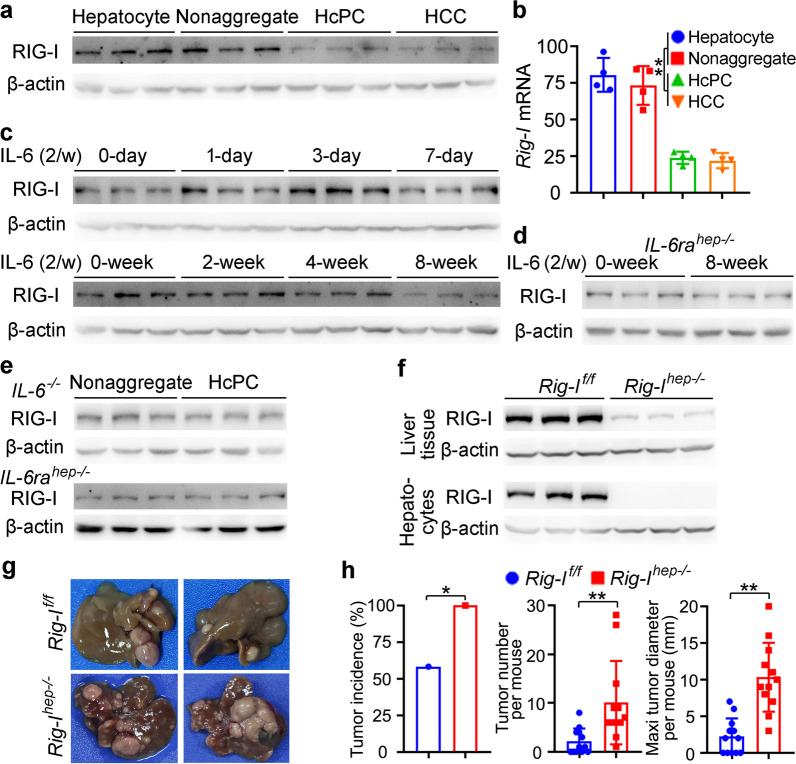
Fig. 1.
IL-6-induced RIG-I decrease in HcPCs promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. a, b RIG-I expression in isolated normal hepatocytes, nonaggregated hepatocytes and HcPCs from male mice five months post-DEN injection, and established HCC cells eight months post-DEN injection was examined by Western blot (a) and qRT-PCR (b, n = 4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). c RIG-I expression was examined in male mouse livers in the indicated time periods post continuous intraperitoneal IL-6 injection twice a week. d RIG-I expression was examined in liver tissues of IL-6rahep−/− mice treated as in c. e RIG-I expression was examined in nonaggregate hepatocytes and HcPCs isolated from male IL-6−/− or IL-6rahep−/− mice five months post-DEN injection. f RIG-I expression in liver tissues and isolated hepatocytes from Rig-Ihep−/− mice was confirmed by Western blot. g Representative livers of DEN-induced HCC in male Rig-If/f and Rig-Ihep−/− mice. h Tumor incidence (chi-square test), number and maximum diameter (unpaired t-test) in g were analyzed (n = 12). Data are shown as mean ± s.d. or photographs from one representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01