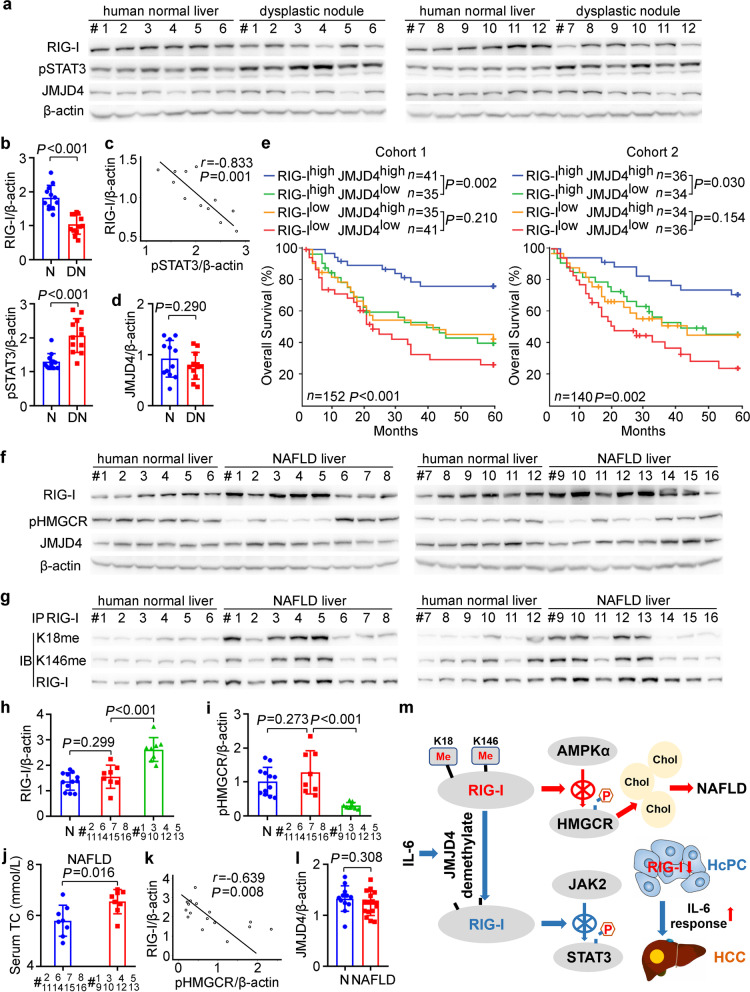
Fig. 7.
RIG-I expression and methylation may be correlated to human hepatocarcinogenesis, prognosis, and NAFLD progression. a RIG-I, JMJD4, and STAT3 phosphorylation were examined in human normal liver tissues and dysplastic nodule tissues from the indicated patients. b Quantified RIG-I expression and STAT3 phosphorylation in human normal liver (N) tissues and dysplastic nodule (DN) tissues were shown (n = 12, unpaired t-test). c The correlation between RIG-I expression and STAT3 phosphorylation in human dysplastic nodule tissues was analyzed by Pearson’s correlation coefficient assay. d Quantified JMJD4 protein level in human normal liver (N) tissues and dysplastic nodule (DN) tissues were shown (n = 12, unpaired t-test). e Kaplan–Meier survival curves of overall survival based on dichotomized RIG-I and JMJD4 mRNA expression in HCC tissues of Cohort 1 and 2. The median levels of RIG-I and JMJD4 expression in each cohort were used as the cutoff, with log-rank test for significance. f RIG-I, JMJD4, and HMGCR phosphorylation were examined in human normal liver tissues and NAFLD tissues from the indicated patients. g Methylated RIG-I at K18 or K146 were examined in the precipitates using RIG-I antibody from human normal liver tissues and NAFLD tissues as in f. h, i Quantified RIG-I protein level (h) and HMGCR phosphorylation level (i) in human normal liver tissues (N, n = 12) and the indicated NAFLD tissues (n = 8, unpaired t-test) were shown. j Serum TC of the indicated NAFLD patients were shown (n = 8, unpaired t-test). k The correlation between RIG-I expression and HMGCR phosphorylation in human NAFLD tissues was analyzed by Pearson’s correlation coefficient assay. l Quantified JMJD4 protein level in human normal liver (N, n = 12) tissues and NAFLD (n = 16, unpaired t-test) tissues were shown. m Working model for the mechanism of constitutive methylated RIG-I at K18 and K146 inhibits HMGCR phosphorylation to promote cholesterol synthesis and NAFLD progression, while IL-6-induced and JMJD4-mediated RIG-I demethylation inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation to suppress hepatocarcinogenesis, and decreased RIG-I in HcPCs enhances IL-6 effects and drives them to established HCC. Data are shown as mean ± s.d., survival curves, or photographs as indicated