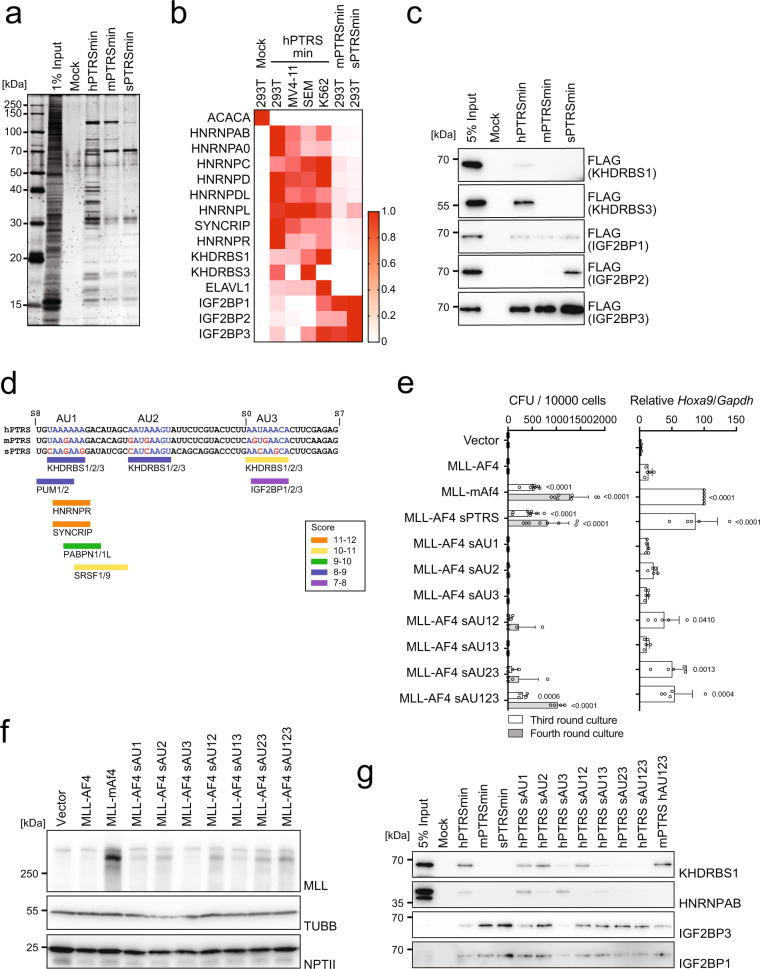
Fig. 4. Unique RNA-binding proteins specifically bind to RNA containing the PTRS.
a Silver staining of purified factors associated with the minimum PTRS of AF4. b Heat map of proteins co-purified with the PTRS RNAs with the relative scores. Proteins were identified using mass spectrometry. c Immunoprecipitation-western blotting of proteins associated with the PTRS RNAs using 293 T cells transiently expressing FLAG-tagged proteins. d CISBP-RNA database analysis of the RNA sequences specifically recognized by various RBPs in the minimum PTRS of human AF4 (http://cisbp-rna.ccbr.utoronto.ca/index.php). The nucleotide bases in the three AU-rich sites are marked in blue letters, whereas the different bases from the human sequence in the three AU-rich sites are in red. e Transforming ability of MLL-AF4 mutants. Various MLL-AF4 constructs carrying synonymous mutations on the AU-rich sites were examined for transformation of HSPCs under an ex vivo myeloid condition, as shown in Fig. 1A (n = 8: Vector, MLL-AF4, MLL-mAf4, MLL-AF4 sPTRS; n = 4: the others). Hoxa9 expression normalized to Gapdh is shown as the relative value of MLL-mAF4 (set to 100) (n = 5). Data are presented as the mean ± SD of indicated biologically independent replicates. P-value was calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. f Western blotting of MLL-AF4 mutants in 293 T cells transfected with the MLL fusion expression vectors shown in (e) (as in Fig. 1d). g Association of endogenous RBPs with the minimum PTRS of AF4. Immunoprecipitation-western blotting was performed using 293 T cells. Endogenous proteins were detected using specific antibodies. Silver staining (a) and Western blotting (c, f, g) were performed on two biological replicates. See also Supplementary Fig. 4. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.