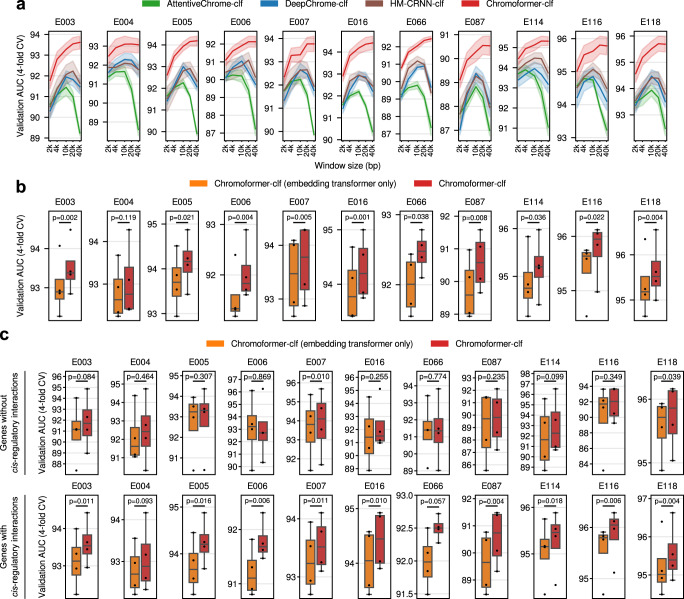
Fig. 3. Contributing factors to the superior performance of Chromoformer.
a Effect of input window size around TSS on the model performance. Chromoformer and the other benchmark models were trained for five different window sizes (2 kbp, 4 kbp, 10 kbp, 20 kbp, and 40 kbp), while all the other training procedures were kept the same as previously. Bold lines denote the average validation AUC across 4-fold cross-validation for each window size, while the shades denote the standard error of them. b Effect of taking distal cis-regulations by pCREs into account. We trained ablated Chromoformer models which only have the Embedding transformer and thus cannot incorporate the cis-regulatory information between the core promoter and pCREs. The resulting cross-validation (n = 4) performances were compared with the intact Chromoformer model. c Comparison of the cross-validation (n = 4) performances for a subset of genes without or with known chromatin interactions. ROC-AUC scores of Embedding transformer-only Chromoformer and intact Chromoformer were computed only for a subset of genes that do not have known cis-regulatory interactions (Upper), and genes with at least one known cis-regulatory interactions. P-values from two-sided paired t-tests are shown. In the boxplot, the center line denotes the median, the upper and lower box limits denote upper and lower quartiles, and the whiskers denote 1.5× interquartile range. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.