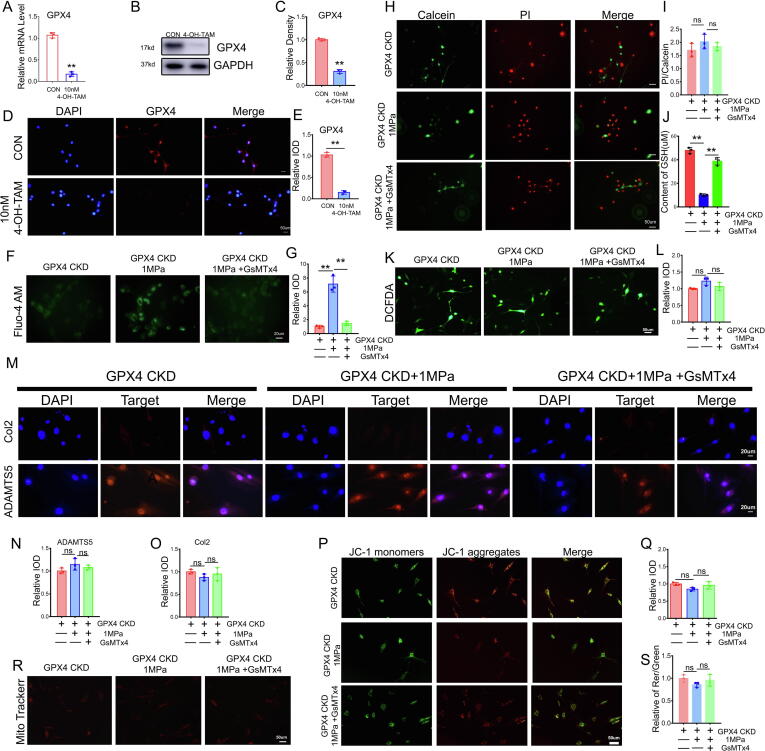
Fig. 5.
Suppression of the Piezo1 channel failed to reverse mechanical overload-induced chondrocyte damage in GPX4-deficient mice. (A). Real-time PCR analysis of GPX4 (n = 3 for each group). (B). Western blot (WB) analysis of GPX4. (C). Quantification of WB analysis (n = 3 for each group). (D). Representative immunofluorescence images of GPX4 in chondrocytes. Scale bars 50 μm. (E). Quantification of immunofluorescence analysis (n = 3 for each group). (F). Calcium influx in chromocytes was tested by Fluo-4 AM of chondrocytes in each indicated group. Scale bars 50 μm. (G). Quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity (n = 3 for each group). (H). Cell death ratio of chondrocytes in each indicated group. Scale bar = 50 μm. (I). The cell number of PI (red fluorescence)/calcein (green fluorescence) reflected the cell death ratio (n = 3 for each group). (J). The expression of GSH in chondrocytes (n = 3 for each group). (K). Representative images of ROS levels in chondrocytes. Scale bar = 50 μm. (L). Quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity (n = 3 for each group). (M). Representative immunofluorescence images of Col2 and ADAMTS-5 in chondrocytes. Scale bars 20 μm. (N-O). Quantification of immunofluorescence analysis (n = 3 for each group). (P). JC-1 assay of chondrocytes. Scale bar = 50 μm. (Q). The relative IOD ratio of red fluorescence to green fluorescence was used for quantitative analysis (n = 3 for each group). (R). Representative fluorescence images of mitochondria in chondrocytes. Scale bar = 50 μm. (S). Quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity (n = 3 for each group). Data were presented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.