Figure 6. Dynamic telomeric R-loops promote D-loop formation in the absence of RAD52.
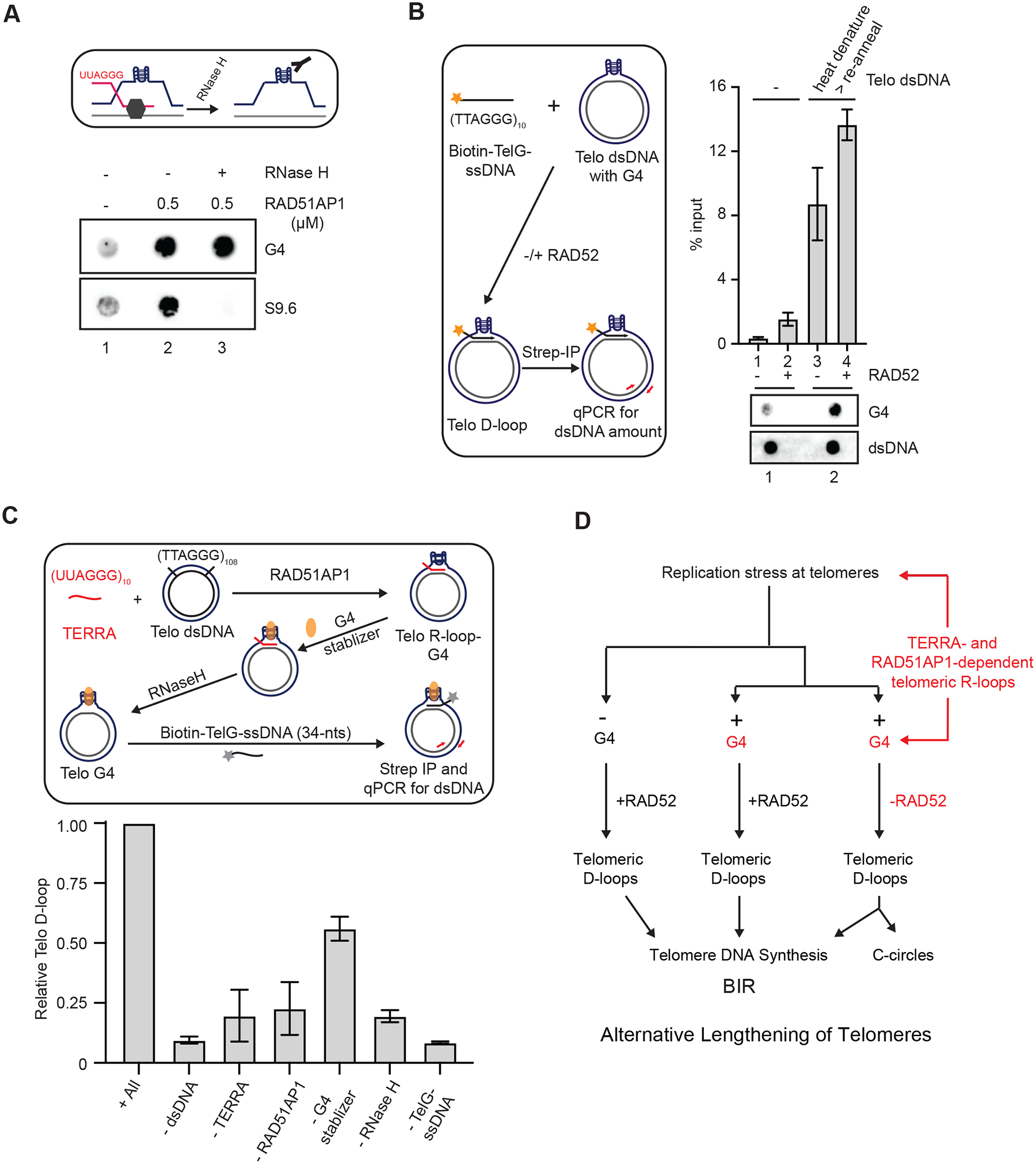
(A) A schematic for testing the presence of G4s in R-loops after removal of DNA:RNA hybrids (upper panel). Telomeric R-loops were generated by incubating TERRA (60-nt, 60 nM), RAD51AP1 (0.5 μM) and dsDNA containing telomeric sequences for 20 min. In lane 3, the sample was treated with RNaseH (0.5 unit) for 5 min after R-loop formation. Reaction products were analyzed for DNA:RNA hybrids and G4s by dot blot using S9.6 and BG4 antibodies, respectively. (B) The experimental scheme to test whether telomeric G4s promote D-loop formation (left). dsDNA containing telomeric sequences was heat denatured and reannealed slowly to increase G4s. The presence of high or low levels of G4s in dsDNA (1 μg) was confirmed by dot blot (bottom panel). The dsDNA harboring high or low levels of G4s was incubated with biotin-TelG-ssDNA (30 nM) in the presence or absence of RAD52 (0.3 μM) for 20 min. Telomeric D-loops were captured with streptavidin beads (10 uL) and quantified by qPCR using primers specific to the dsDNA. Error bars: SEM, n=2. (C) The experimental scheme to reconstitute the TERRA-and RAD51AP1-mediated formation of telomeric D-loops (upper panel). Telomeric R-loops were generated by incubating TERRA (60-nt, 60 nM), RAD51AP1 (0.3 μM) and dsDNA containing telomeric sequences. PDS (1 mM) was added to stabilize G4s, and the DNA:RNA hybrids in R-loops were removed by RNaseH (0.5 unit, 5 min). Subsequently, biotin-TelG-ssDNA was added, and the resulting D-loops were captured with streptavidin beads (10 μL) and quantified by qPCR. Error bars: SEM: n=3. The effects of omitting individual components of the reaction were tested. (D) A model in which the dynamic telomeric R-loops assembled by TERRA and RAD51AP1 promote G4 accumulation and D-loop formation, enabling the RAD52-independent ALT pathway.
