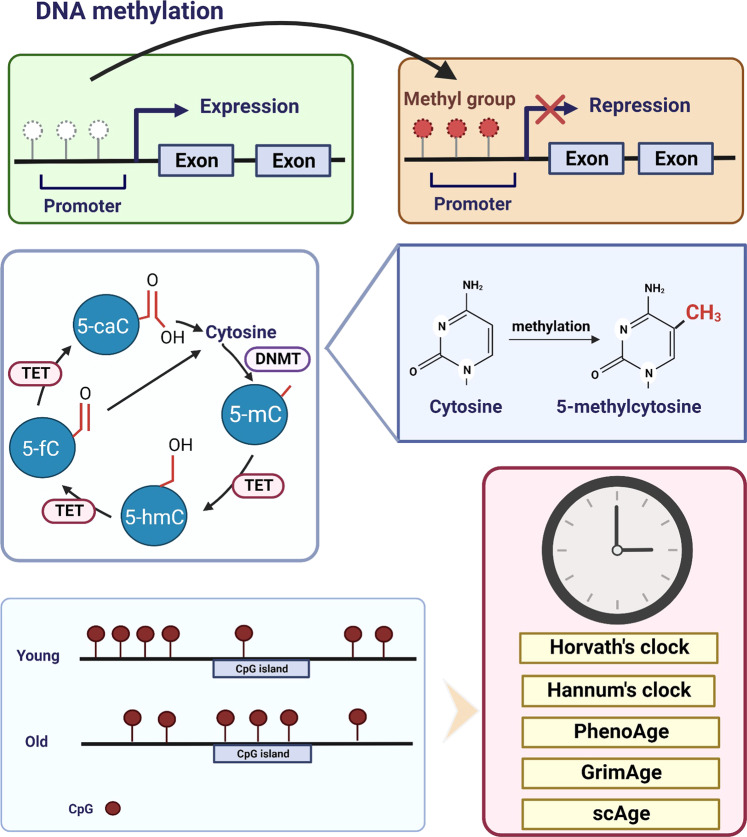
Fig. 3.
The mechanism of DNA methylation and the epigenetic clock theory of aging. Aging is often marked by global DNA hypomethylation, but hypermethylation also occurs at selective CpG islands. DNA methylation at the promoter of a gene often leads to silencing of that gene. DNA methylation at the 5ʹ cytosine of CpG results in 5-methylcytosine (5-mC). The methylation of DNA is mediated by DNMTs whereas the methyl group on DNA is removed by TET enzymes. TET enzymes oxidize 5-mC to generate 5-mC derivatives, including 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5-fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (5-caC), in mammalian cells. Age estimators, such as Horvath’s clock, Hannum’s clock, PhenoAge, GrimAge and single-cell age clock (scAge) are based on DNA methylation changes in the genome