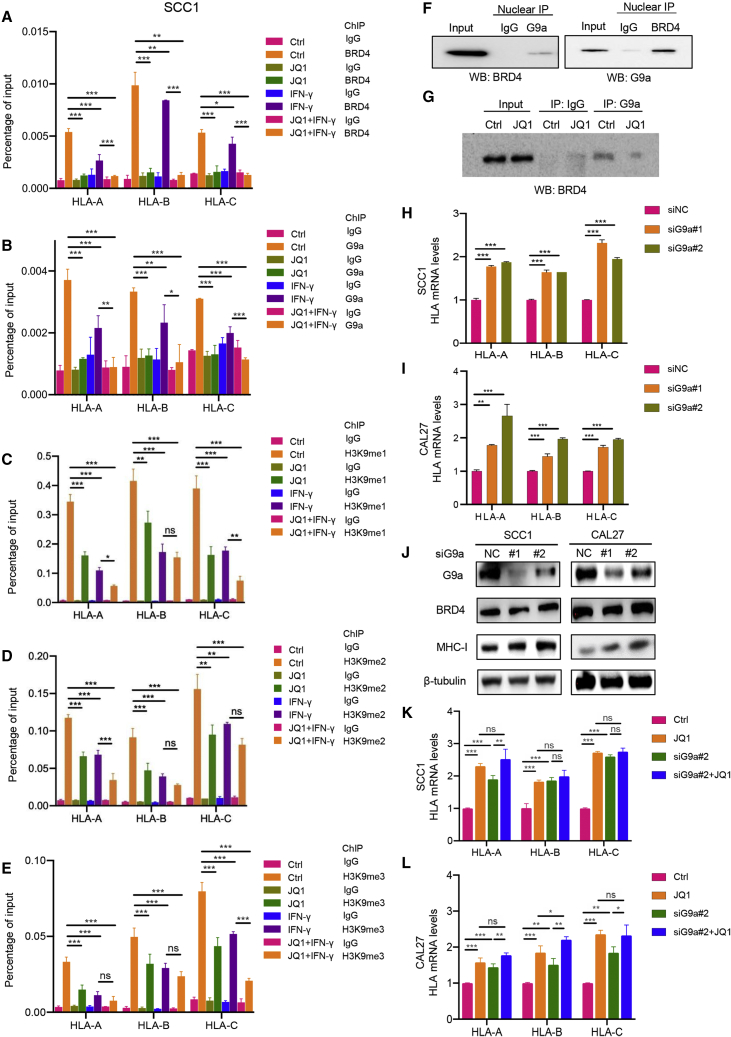
Figure 5.
BRD4 inhibition enhances MHC class I antigen presentation molecules through suppressing G9a in HNSCC
(A–E) SCC1 cells treated with JQ1 and/or IFN-γ were subjected to ChIP assay with BRD4, G9a, H3K9me1, H3K9me2, and H3K9me3 antibodies. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA. ns, non-significant. (F) Nuclear proteins extracted from SCC1 cells were subjected to reciprocal immunoprecipitation with G9a and BRD4 antibodies. (G) Nuclear proteins extracted from SCC1 cells treated with or without JQ1 were subjected to immunoprecipitation with G9a and BRD4 were detected. (H and I) RT-qPCR showed that the expression of HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C in SCC1 and CAL27 cells transfected with siRNA targeting G9a. Means ± SDs were shown. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA. (J) Western blot showed the expression of MHC class I in SCC1 and CAL27 cells transfected with siRNA targeting G9a. (K and L) RT-qPCR showed the expression of HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C in SCC1 and CAL27 cells treated with JQ1 and siRNA targeting G9a. Means ± SDs are shown. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA.