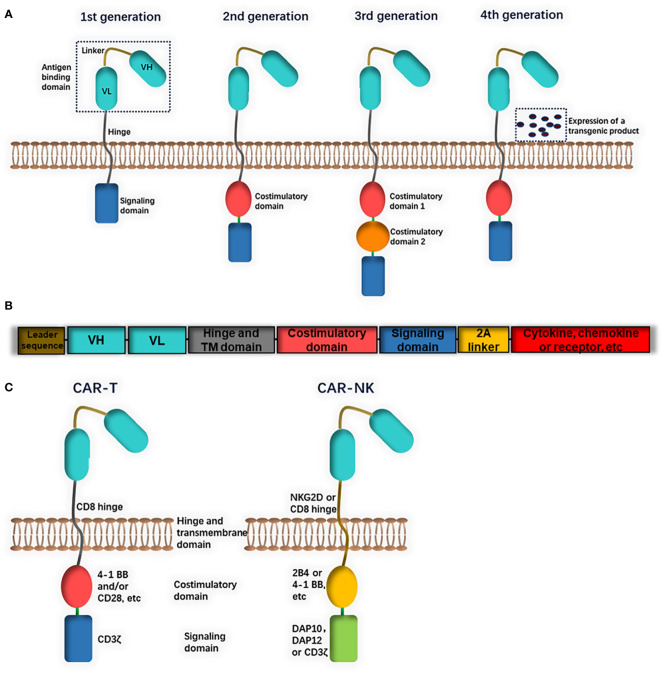
Figure 1.
The structure of chimeric antigen receptors (CAR). (A) CAR consist of an extracellular antigen binding domain, a transmembrane hinge and intracellular domain. The extracellular domain could be a single chain fragment of variable region (ScFv) antibody or a functional domain of specific ligand. The intracellular domain is composed of a signaling domain (first generation) and one costimulatory domain (second generation) or two (third generation). (B) Fourth generation CARs include a constitutive or inducible expression of a transgenic product (cytokine, chemokine or receptor, etc.). (C) Differences in CAR constructs between CAR-T and CAR-NK: CAR-T cells usually contains a CD8 transmembrane domain, CD3ζ signaling domain and 4-1BB and/or CD28 costimulatory domain. CAR-NK cells may be with different domains (for example, NKG2D transmembrane domain, DAP10 or DAP12 signaling domain and 2B4 costimulatory domain).