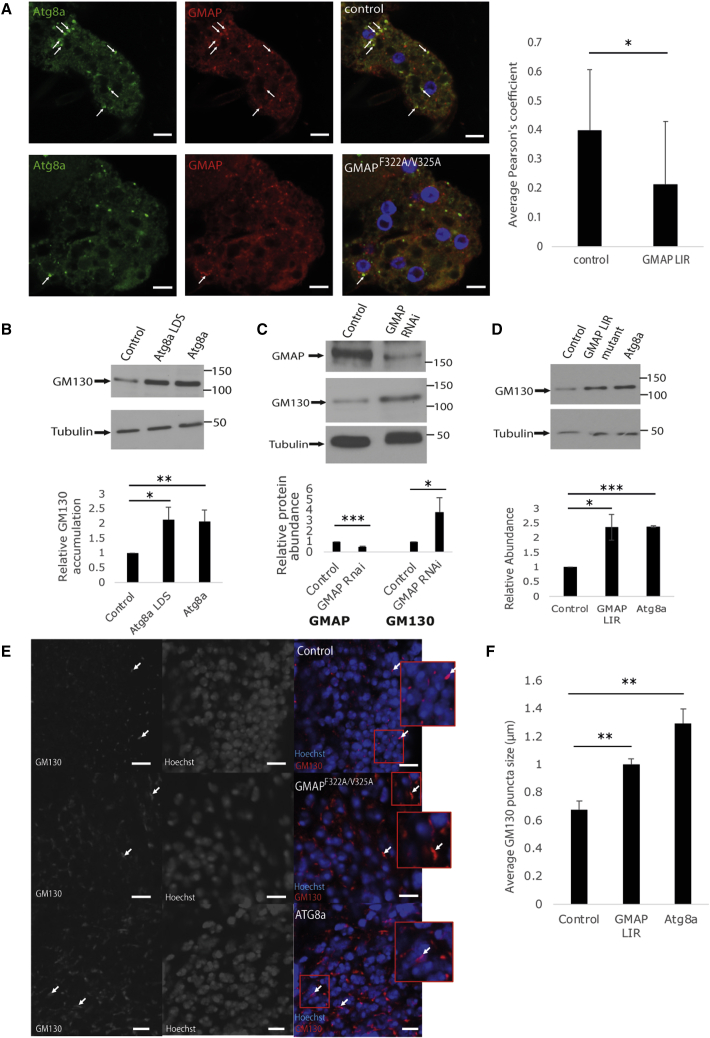
Figure 5.
GMAP regulates Golgi turnover via autophagy
(A) Confocal images showing co-localization of endogenous Atg8a and the GMAP under starvation conditions in adult fat body in control and GMAP F322A/V325A mutant flies.
(B) Western blots showing accumulation of the Golgi marker GM130 in Atg8a KG07569 and Atg8aK48A/Y49A mutant flies compared with wild-type flies.
(C) Western blots showing accumulation of GM130 in GMAP-RNAi lines compared with control RNAi and its quantification shown below.
(D) Western blots showing accumulation of GM130 in GMAP F322A/V325A mutant flies compared with wild-type flies.
(E) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of Drosophila brain showing increased accumulation of the cis-Golgi marker (GM130) and the altered morphology of Golgi in GMAP F322A/V325A and Atg8a KG07569 mutant flies. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(F) Average GM130 puncta size is larger in GMAP F322A/V325A and Atg8a KG07569 mutant flies compared with wild-type flies. Bar charts show means ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using two-tailed Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Number of biological repeats (N = 3 for all figures). Genotypes: (A) Control: w1118/Y, GMAP: GMAP F322A/V325A/Y. (B) Control: w1118/Y, Atg8a LDS: Atg8a K48A/Y49A/Y, Atg8a: Atg8a KG07569/Y. (C) Control: yw1118;P{attP,y[+],w[3`]}/+;da-GAL4/+, GMAP-RNAi: GMAP-RNAi/+; da-GAL4/+. (D and E) Control:w1118/Y, GMAP: GMAP F322A/V325A/Y, Atg8a: Atg8a KG07569/Y.