Figure 6. YTHDC1 and CPSF4 competitively bind to FIP1L1 and regulate the choice of APA sites.
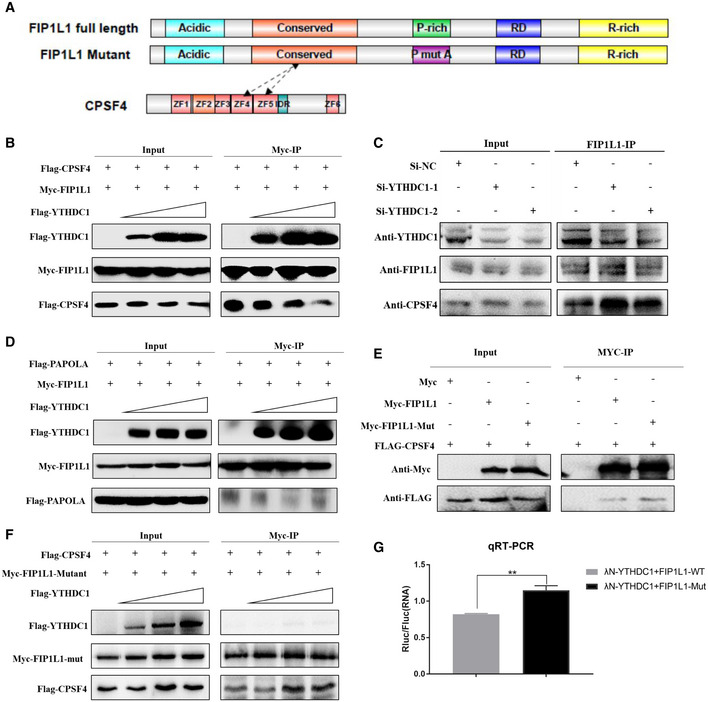
- Schematic diagram of functional regions of FIP1L1 and CPSF4.
- YTHDC1 inhibits the interaction between Myc‐FIP1L1 and FLAG‐CPSF4. A substantially suppressed level of interaction between Myc‐FIP1L1 and FLAG‐CPSF4 was observed when FLAG‐YTHDC1 input was increased.
- Knockdown of YTHDC1 enhances endogenous FIP1L1 recruitment to CPSF4, indicating that YTHDC1 plays an important role in interfering with the 3′ end processing complex interaction.
- YTHDC1 has little effect on the interaction between Myc‐FIP1L1 and FLAG‐PAPOLA. The interaction between Myc‐FIP1L1 and FLAG‐PAPOLA was not significantly affected when FLAG‐YTHDC1 was increased.
- Mutation of proline had little effect on the interaction between FIP1L1 and CPSF4 compared with the wild type.
- The mutation of prolines in FIP1L1 abrogated the inhibitory effect of YTHDC1 on the interaction between FIP1L1 and CPSF4.
- qRT–PCR validation of APA site switching in a bicistronic dual luciferase system. FIP1L1‐Mut could significantly increase the ratios of Rluc/Fluc compared to FIP1L1‐WT, indicating that YTHDC1 inhibits the use of proximal APA sites by interacting with the proline‐rich domain of FIP1L1. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three biological replicates. **P = 8.77 × 10−4, the P values were obtained with unpaired two‐tailed Student's t‐test.
Source data are available online for this figure.
