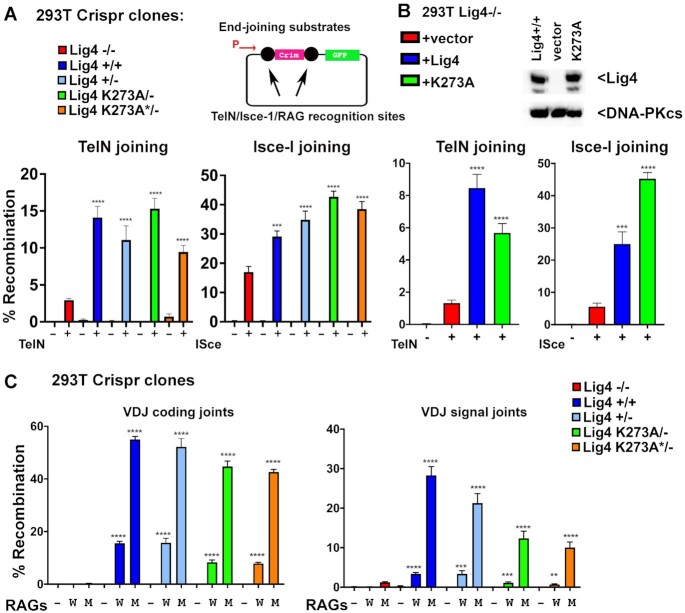
Figure 2.
Catalytically inactive Lig4 promotes joining of DSBs in episomal substrates in 293T cells. (A) Fluorescent substrates (depicted in top panels indicate promoter with arrow) were utilized to detect TelN, I-SceI, or VDJ coding and signal joints in 293T cells of the indicated genotypes. 293T clones with the indicated genotypes were co-transfected with TelN or I-SceI plasmid substrate, with and without enzyme (−/+) and analyzed for red/green fluorescence via flow cytometry (lower panels). (B) Lig4−/− 293T cells were tested for TelN and I-SceI joining by co-transfecting the TelN/I-SceI substrates and expression plasmids with or without co-transfection of expression plasmids encoding either WT or catalytically inactive human Lig4 as indicated. (C) 293T clones were co-transfected with wild-type (W) or hypermutant (M) RAG expression plasmids with either plasmid substrates to detect coding or signal end-joining as indicated by analysis of red/blue fluorescence via flow cytometry. Episomal VDJ assays testing joining of coding (hairpin) and signal (blunt) ends. Cells were transfected with substrate and either: no Rag2 (−), WT rags (W), or mutant rag2 (M) and analyzed via flow cytometry. In A, B, and C, student's T test comparing joining rates between Lig4−/− and either Lig4+/+, Lig4+/−, or K273A were performed; ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; ns = not significant in two-tailed unpaired t test.