Figure 6.
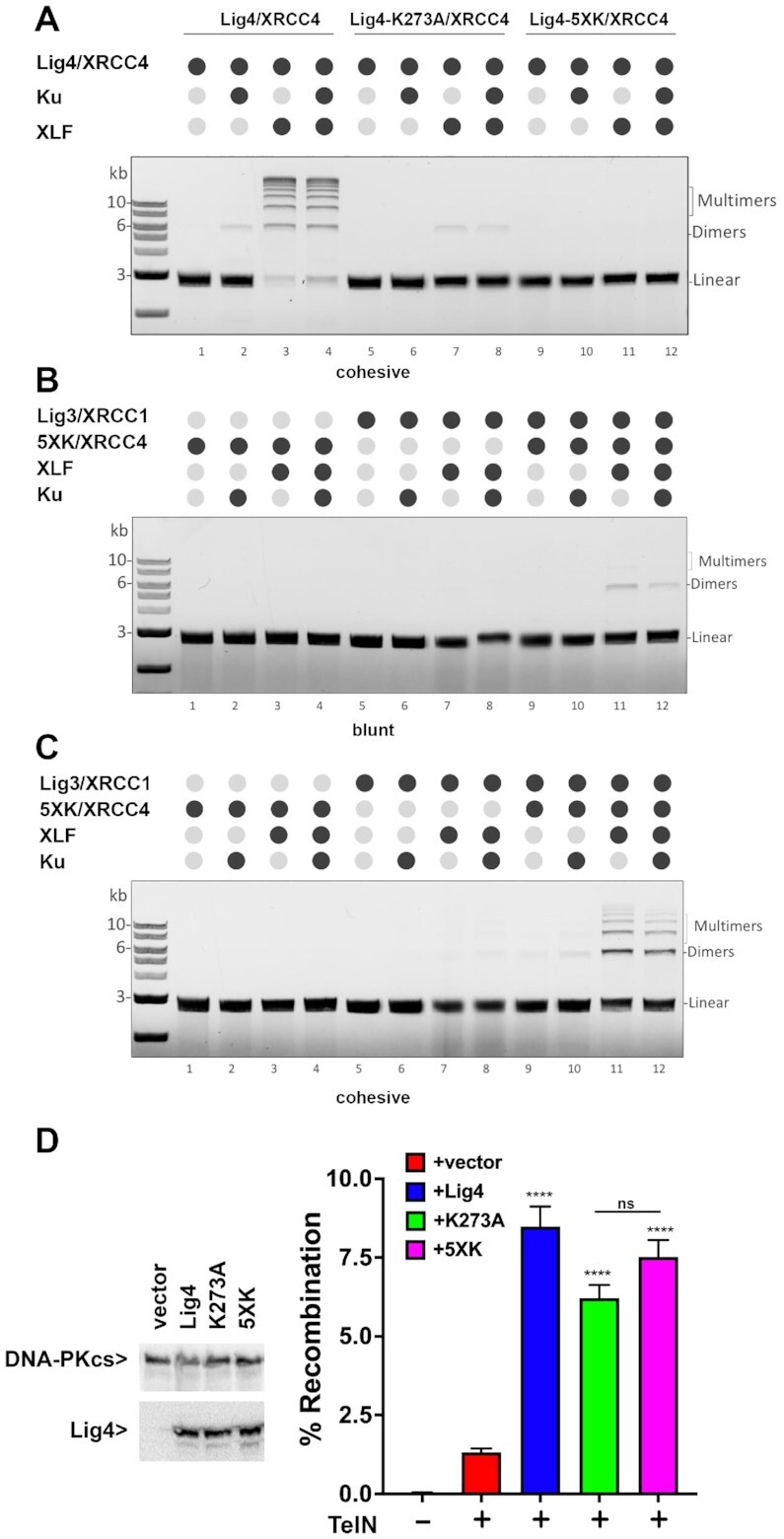
The 5XK Lig4 mutant has no residual ligation activity but stimulates Lig3 joining in vitro, and promotes end-joining in living cells. (A) DNA ligation assay using a linear DNA fragment (2.7 kb) with cohesive ends and NHEJ components as indicated. (B + C) Lig3 stimulation assay with 5XK mutant using a linear DNA fragment (2.7 kb) with (B) blunt ends or (C) cohesive ends. Assays were performed using 250 nM 5XK Lig4 and Ku, 200 nM XLF and 40 nM Lig3 as final concentration. Ligation products were deproteinized and resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis before staining with ethidium bromide and detection. (D) (left) Immunoblot of cells transfected with indicated expression plasmids, and probed for either Lig4 or DNA-PKcs. (right) Lig4−/− 293T cells were tested for TelN joining by co-transfecting the TelN substrates and expression plasmids with or without co-transfection of expression plasmids encoding either WT, K273A, or 5XK mutant. Student's T test comparing joining rates between vector and Lig4, K273A or 5XK were performed; ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; ns = not significant in two-tailed unpaired t test.
