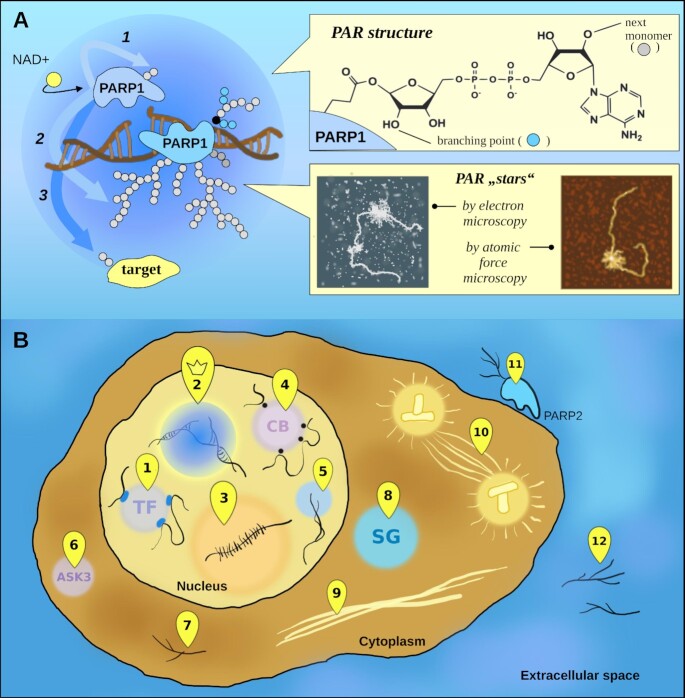
Figure 4.
PAR synthesis and cellular localization. (A) PARPs is performs the PARylation reaction in the form of 1. Intramolecular (in cis-) auto-modification, 2. Intermolecular (in trans-) auto-modification within PARP dimers and 3. trans-modification of non-PARP targets. The points of active PAR production—PAR ‘stars’—are detected by electron microscopy (95,96) or atomic force microscopy (97). (B) PAR is found in cells at several locations: 1.transcription factories; 2. DNA repair foci; 3. the nucleolus; 4. Cajal bodies; 5. telomeres; 6. ASK3 condensates; 7. in the form of protein-free PAR chains; 8. stress granules; 9. pathological aggregates; 10. the spindle; and in extracellular space as 11. a product of PARP2 located on T-cell surface; 12. free PAR chains released in the extracellular matrix due to cell necrosis.