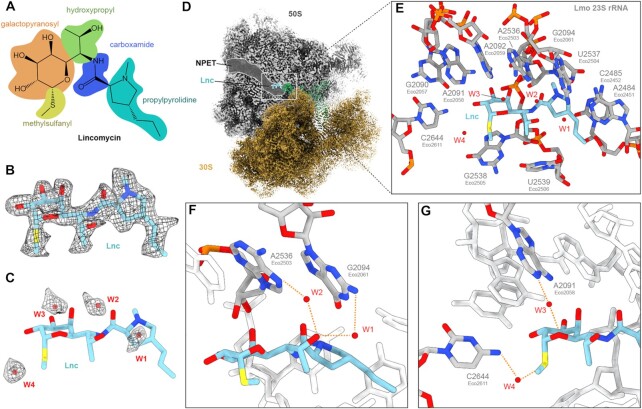
Figure 4.
Cryo-EM structure of the L. monocytogenes lincomycin-70S complex. (A) Chemical structure of lincomycin, with galactopyranosyl (orange), methylsulfanyl (yellow), hydroxypropyl (green), carboxamide (blue) and propylpyrrolidine (cyan) moieties highlighted. (B) Cryo-EM density (mesh) with molecular model of lincomycin (Lnc, blue). (C) Molecular model of Lnc (blue) with cryo-EM density (mesh) and model for waters W1-W4 (red). (D) Cryo-EM density of L. monocytogenes Lnc-70S complex with Lnc bound at the PTC, adjacent to the ribosomal NPET in the 50S (grey) subunit. (E) Lnc (blue) with surrounding waters W1-W4 (red) and 23S rRNA nucleotides (grey). (F) Water-mediated interaction of the hydroxypropyl-group of Lnc (blue) with N2 of G2094 (EcoG2061, grey) through W1 (red) and N7 of A2536 (EcoA2503, grey) through W2 (red). (G) Water-mediated interaction of Lnc (blue) with N1 of A2091 (EcoA2058, grey) and W3 and N4 of C2644 (EcoC2611, grey) with W4 (red).