Figure 5: KynA promotes ATP synthase dimerization and ATPIF1 is required for KynA-induced ischemic protection.
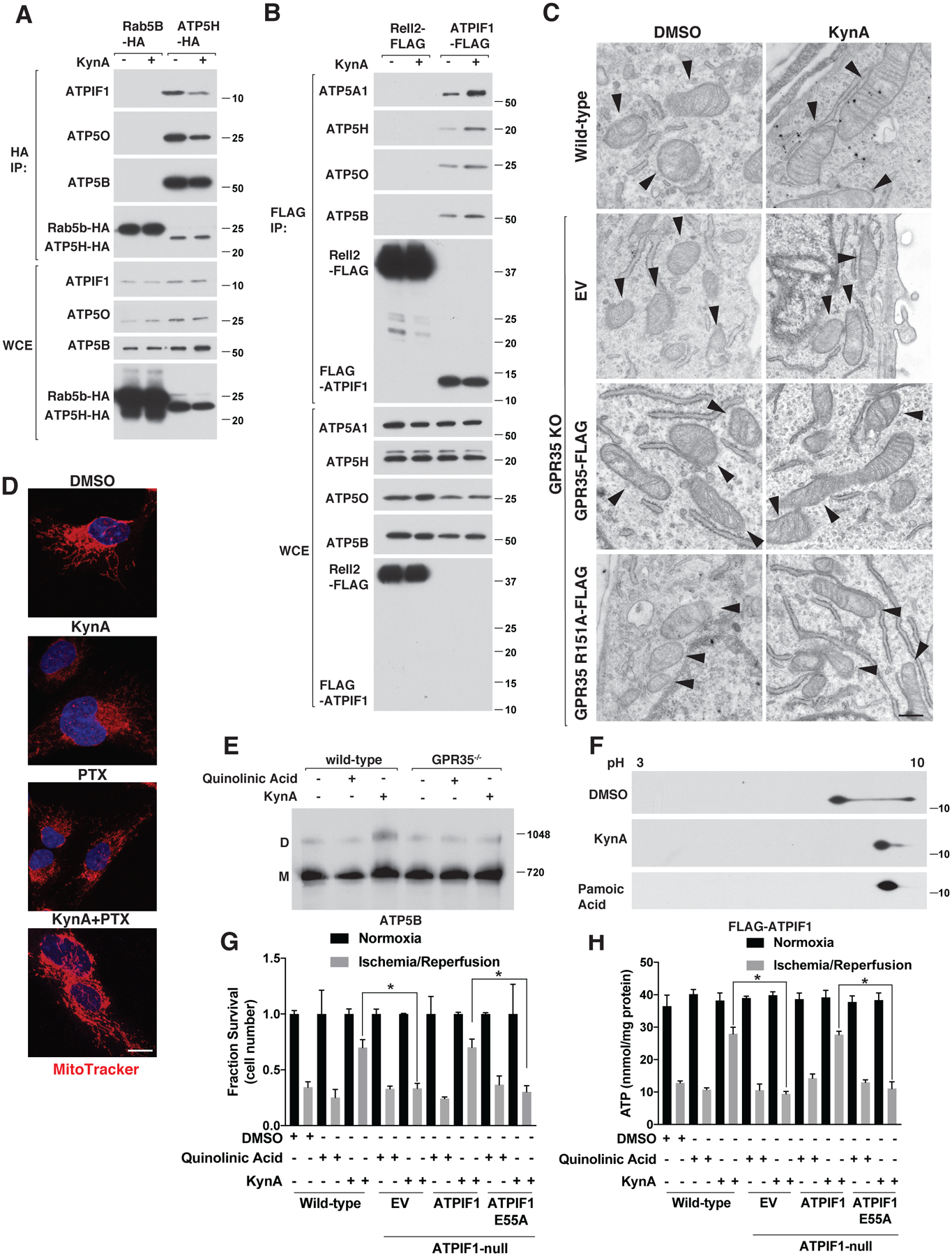
(A) Immunoblot analysis of anti-HA immunoprecipitates (HA-IP) and whole cell extracts (WCE) from mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes stably expressing Rab5B-HA or ATP5H-HA that were or were not treated with 20 μM KynA for 20 mins. (B) Immunoblot analysis of anti-FLAG immunoprecipites (FLAG-IP) and whole cell extracts (WCE) from mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes stably expressing Rell2-FLAG or FLAG-ATPIF1 that were or were not treated with 20 μM KynA for 20 mins. (C) Electron micrographs of wild-type and GPR35 −/− cardiomyocytes stably expressing GPR35-FLAG, R151A GPR35-FLAG, or empty vector (EV) that were treated with 20 μM KynA or DMSO for 20 mins. Arrowheads indicate mitochondria. Scale bar indicates 500 nm. (D) Live cell fluorescence imaging of mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes treated with 20 μM KynA, 200 ng/mL pertussis toxin (PTX), or both prior to staining with 100 nM Mitotracker FM. Scale bar indicates 20 μm. (E) Blue-native page analysis of mitochondria isolated from mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes treated with 20 μM quinolinic acid, 20 μM KynA, or DMSO for 20 mins. (F) Anti-Flag immunoblot analysis after two-dimensional gel-electrophoresis of cell extracts made from mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes stably expressing FLAG-ATPIF1 that were treated with 20 μM KynA, 1 μM pamoic acid, or DMSO for 20 mins. (G and H) Fractional survival (G) and ATP levels (H) of wild-type and ATPIF1−/− human IPS-derived cardiomyocytes stably expressing wild-type or E55A ATPIF1, or the empty vector (EV), that were pretreated with 20 μM KynA, 20 μM quinolinic acid or DMSO for 1 hr prior simulated I/R ex vivo. Shown are mean −/+SD. * indicates P value <0.05.
