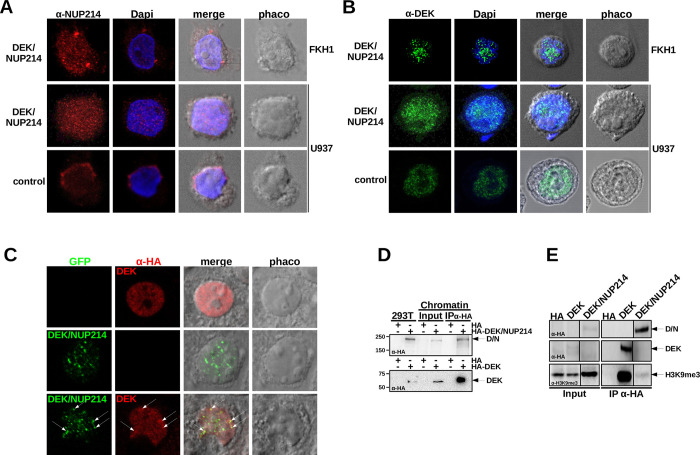
Fig 1. Localization of NUP214, DEK, and DEK/NUP214.
A. Localization of NUP214 in t(6;9)-AML cells FKH1 and U937 cells stably expressing DEK/NUP214 and U937 control cells—CLSM: red fluorochrome–Alexa 594-conjugated secondary Ab detecting the anti-NUP214 Ab; Dapi–Hoechst 3334 staining; phaco–phase contrast; merge–digital superposition. B. Localization of DEK and DEK/NUP214 in t(6;9)-AML cells FKH1 and U937 cells stably expressing DEK/NUP214 and U937 control cells–CLSM: green fluorochrome—Alexa 488-conjugated secondary Ab detecting the anti-DEK Ab. Dapi–Hoechst 3334 staining; phaco–phase contrast; merge–digital superposition. C. colocalization of DEK and DEK/NUP214 in transfected 293T cells; red fluorochrome–Alexa 594-conjugated secondary Ab detecting the anti-HA Ab detecting HA-tagged DEK; green fluorochrome–GFP signal of the GFP-tagged DEK/NUP214; phaco–phase contrast; merge–digital superposition. D. Chromatin-IP of DEK and DEK/NUP214. HA-tagged DEK and DEK/NUP214 transfected into 293T cells. Immunoblot anti-HA, Input– 10% of chromatin/protein lysate used for the IP. E. Co-IP anti HA between HA-tagged DEK or DEK/NUP214 and intrinsic H3K9me3 in 293T cells. Input– 10% of the cell lysate used for the Co-IP. The immunoblot was stained either with the anti-HA Ab (for detecting DEK and DEK/NUP214) or the anti- H3K9me3 Ab.