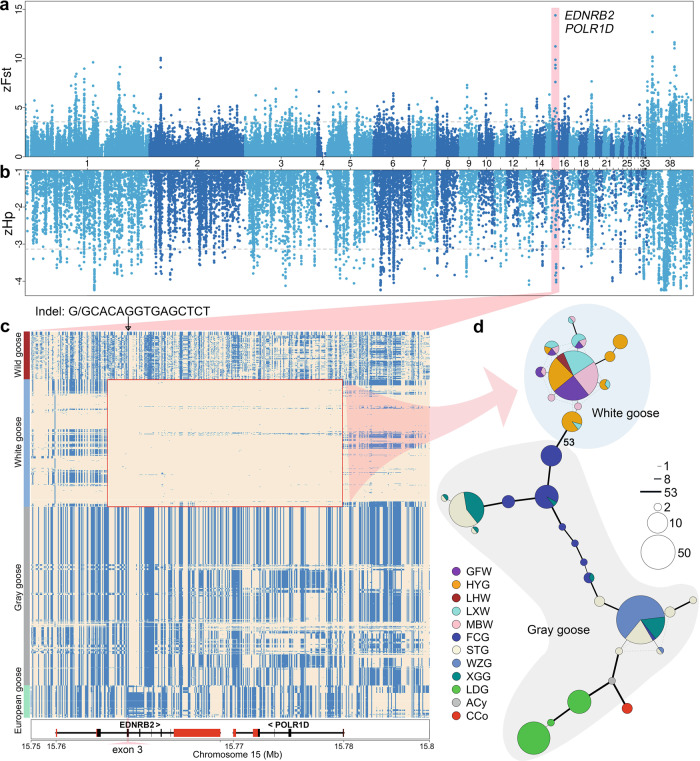
Fig. 4. Selective signals for the white plumage phenotype of geese.
a Manhattan plot of zFst between white and gray geese. The x-axis of the Manhattan plot shows the ordered chromosome that is defined in Supplementary Table 2, and 38 represents Z chromosome. b Manhattan plot of zHp in white geese, with the positions matching zFst. The gray dashed line represents the top 1% cutoff. c The plot of the haplotype structure of variants around the EDNRB2 and POLR1D genes in all domestic geese and wild populations (The genera Anser and Cygnus in the Anatidae family). Major and minor alleles in GFW are indicated by beige and light blue, respectively. The red box represents the unique haplotypes of white geese. The black arrow indicates the position (15,764,637 bp) of the candidate causal 14-bp insertion for the white geese. The red and black rectangles in the bottom box represent the UTRs and CDSs, respectively. d Haplotype network based on 285 SNPs and Indels from the EDNRB2 gene (15,763,328 bp) to POLR1D gene (15,779,122 bp) on chromosome 15. Each circle represents a haplotype, and the size of the circle is proportional to the haplotype frequency. The line width and length represent the difference between haplotypes. GFW Guangfeng white goose, HYG Huoyan goose, LHW Lianhua white goose, LXW Lingxian white goose, MBW Mingbei white goose, FCG Fengcheng gray goose, STG Shitou goose, WZG Wuzong goose, XGG Xingguo gray goose, LDG Landaise goose, ACy Anser cygnoides, CCo Cygnus columbianus.